Hash-based message authentication code (or HMAC) is a cryptographic authentication technique that uses a hash function and a secret key.
With HMAC, you can achieve authentication and verify that data is correct and authentic with shared secrets, as opposed to approaches that use signatures and asymmetric cryptography.
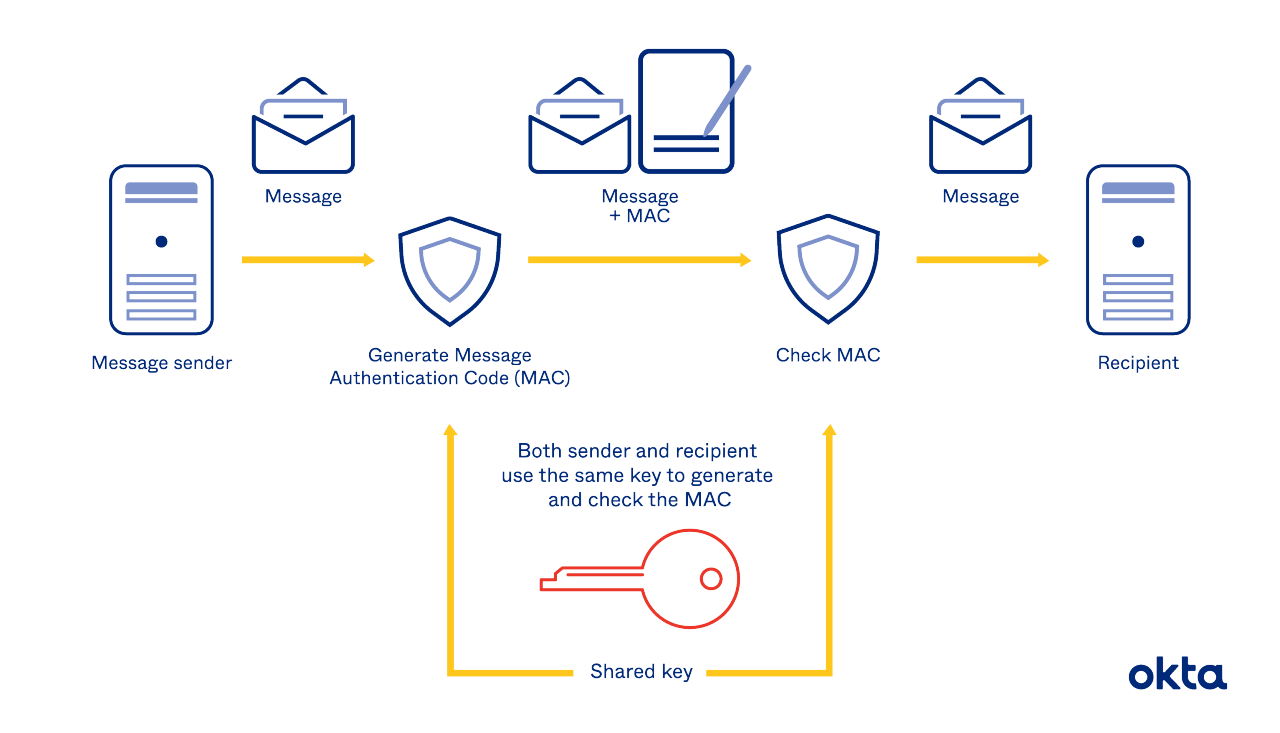
How HMAC Works
Two parties want to communicate, but they want to ensure that the contents of their connection remain private. They also distrust the internet, and they need a way to verify that the packets they receive haven't been tampered with. HMAC is a valid solution.
HMAC keys consist of two parts. These are:
- Cryptographic keys. An encryption algorithm alters data, and a recipient needs a specific code (or key) to make it readable once more. HMAC relies on a shared sets of secret keys.
- Hash function. A hash algorithm alters or digests the message once more. HMAC uses generic cryptographic hash functions, such as SHA-1, MD5, or RIPEMD-128/60.
A pair using this system must agree on:
- Secret keys. They must have a way to decode messages they get. A secret key handles this task, and it's meant to stay secret and hidden.
- Algorithm. They must pick one hash function that all of their messages will move through.
When complete, the message is considered irreversible, and it's also resistant to hacking. Someone who intercepts this message won't even be able to guess at its length. The work renders the message contents absolutely useless to anyone without a key or a code.
HMAC tester tools can help demonstrate how something like this works. Imagine you're dealing with these inputs:
- Potential message: I would like to buy 100 units.
- Secret key: 666
- Algorithm: MD5
The resulting message reads: " fd9f18089206e67b163771a3883185ab."
A dense layer of mathematics underlies what seems like an easy translation process. When we attempt to display what HMAC looks like mathematically, we use diagrams like this.
Understanding the math is critical for developers. If you're asked to explain your work and the protections you offer, a diagram can often showcase things better than your words ever can.
But the average computer user may never need to understand the math. To them, knowing that their messages are protected may be all they require.
How to Implement HMAC
To use HMAC, either as an individual or a web developer, you'll need three important things. And you'll need an agreement about those items with your recipients, so you're all using the same tools at the same time.
These are the two items you'll need:
- A shared secret
- A hashing tool
Only your server should know all three items for all of your users. And that data should be fiercely protected. Anyone who knows the secret keys for your members can take over your server and/or send fraudulent data.
Every website and coding environment is different, but walking through an example might be helpful. Imagine that you'd like to use HMAC on traffic that comes to your website via dynamic ads from Google. You will:
- Build your token in Ad Manager. You'll specify details about the visit and the time. You'll use Google's authentication key to create your "secret key."
- Implement. You can put your new token within your authorization request header, or you can pass it as a query string or form data parameter.
Google makes this process quick and easy. Developers can access a simple tutorial and copy code within minutes.
Notice that you're not asking your Google Ads visitors to memorize a code or do any decoding. The user's server understands the coding requirements within your website, and all of the token setting and translation is invisible to the user.
Even so, you should test this environment often before you deploy it. If you encounter a coding error, you could block people from accessing your site, as it will seem as though they're fraudulent actors. It pays to test any system like this on multiple devices before you set it loose on the wider world.
When Should You Use HMAC?
Nearly every company has sensitive information. If you take in payments of any sort, for example, you likely have credit card data at your fingertips. And if you have employees, you have Social Security numbers that could be stolen.
But some companies have even deeper issues. If you're in a heavily regulated environment, such as health care, or you deal with trade secrets, such as munitions, it pays to move past traditional security measures.
HMAC, with its dual levels of protection, could be ideal for companies that need to do a little more to prove that they're protecting their assets as carefully as possible.
Help From Okta
At Okta, we believe in customized security solutions to help our clients thrive. Learn how Okta uses HMAC signature algorithms to keep your organization secure.
References
HMAC: Keyed-Hashing for Message Authentication. (February 1997). Network Working Group.
HMAC and Key Derivation. Practical Cryptography for Developers.
HMAC Generator/Tester Tool. FreeFormatter.
How API Request Signing Works (And How to Implement HMAC in NodeJS). (2016). Andrew Hoang.
Implement HMAC Authentication (Beta). Google Ad Manager Help.


