Active Directory is a Microsoft product used to organize IT assets like users, computers, and printers. It integrates with most Microsoft Office and Server products.
Lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) is a protocol, not a service. LDAP is used to talk to and query several different types of directories (including Active Directory).
What Is Active Directory?
Microsoft creates a lot of IT software, from Windows desktops to Windows Server, Exchange, Sharepoint, and more.
In the IT environment, users don’t want to use a separate password for each application they access. And IT admins want to be able to group people together and manage access to computers and printers.
Active Directory was created to ease the management of users and computers by storing information about them in a single directory.
Imagine working at a company without a directory:
- You would have to keep providing a username and password for each application.
- IT admins would have to manually assign you to every single application you need to access.
- If you update your password or change your last name, you would have to do that in every application in which you have an account.
The directory brings together, in a central service, information about all the people, computers, and other assets in the organization. It also stores credentials (like your username and password) so it can authenticate you to all the applications you use.
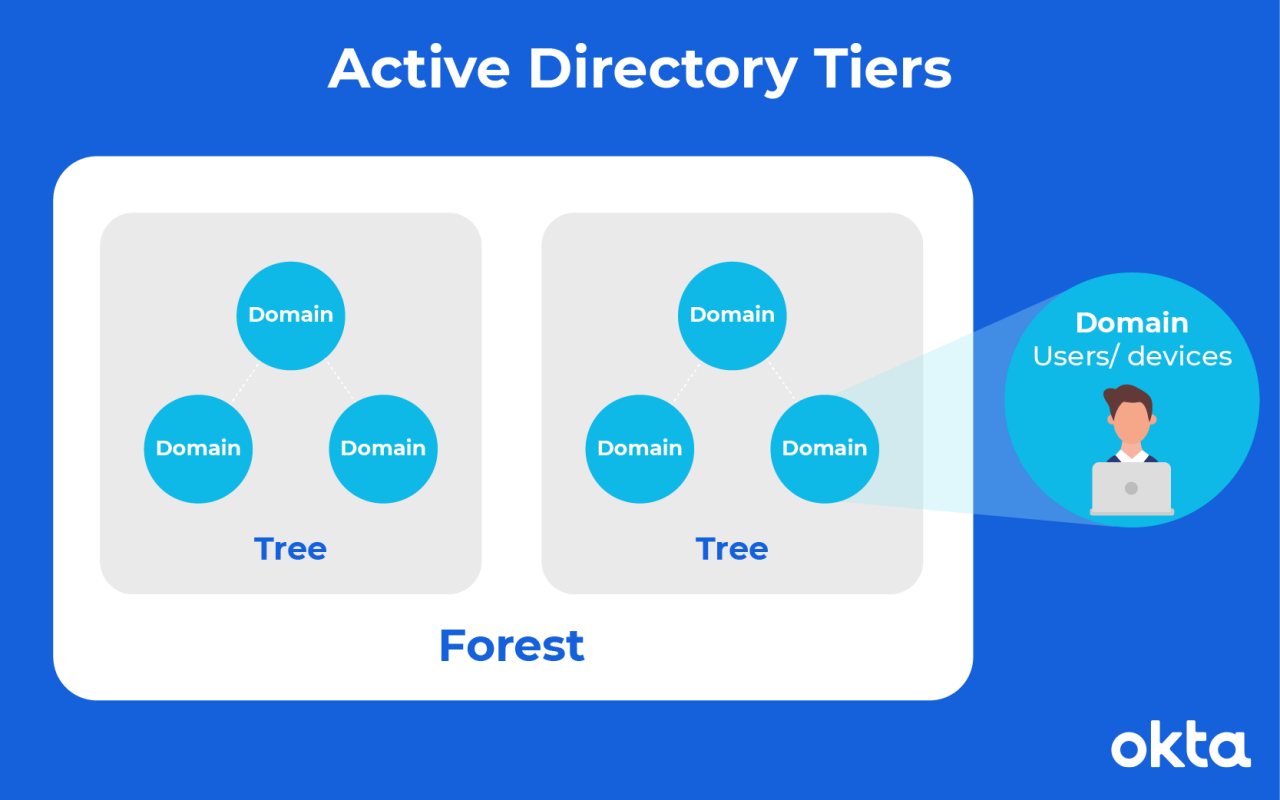
In Active Directory, assets are sorted into one of three tiers.
- Domains: Users (such as employees) and devices (such as computers) that share the same Active Directory database are part of a domain. A domain is usually associated with either a company or an organization in a company, like the “Engineering Domain.”
- Trees: Trees define the trust between domains, deciding who can access what in different parts of an organization, and letting IT admins manage their own community of users and devices.
- Forests: For large organizations or intercompany relationships, domains are grouped into forests. Inter-forest trust is usually developed after a company acquires another company. Employees in both organizations need to access each other's resources.
Each one of these levels has access rights and communication privileges unique to it.
Active Directory also includes security features, including:
- Authentication. Users must provide the relevant credentials before they can access resources on the network.
- Security groups. IT admins organize users into groups. The groups are then assigned to apps to minimize administration.
- Group policy. There are a large number of policies in Active Directory that define who can access computers remotely or configure browser security settings.
Active Directory supports a variety of ways to authenticate users. Over the range of its life, Active Directory has supported LAN Manager, NTLM, and Kerberos. Each time, the authentication protocol evolved to be more usable and secure.
Active Directory’s main purpose was to bring together all the Microsoft technologies to allow users to easily access resources and to allow administrators to securely define their access.
What Is LDAP?
LDAP is a protocol that was designed for applications to query user information very quickly and at scale. It was ideal for something like the telecommunications or airline industry.
Active Directory was designed for enterprises with maybe a few thousand employees and computers. LDAP was a protocol designed for applications powering the telephone wireless carriers that needed to handle millions of requests to authenticate subscribers to the phone networks.
LDAP is a product-agnostic protocol. Active Directory actually implemented with LDAP support to allow LDAP-based applications to work against an existing Active Directory environment.
As a protocol, LDAP is primarily concerned with:
- Directory structure. Each entry in the directory has attributes and can be accessed via a unique distinguished name (DN) that is used when querying the directory.
- Adding, updating, and reading data. LDAP is optimized for fast searching and reading of data.
- Authentication. In LDAP, you “bind” to the service. This authentication can be a simple username and password, a client certificate, or a Kerberos token.
- Search. One area where LDAP excels is search. Again, LDAP-based servers are typically designed for mass queries, and those are usually searches for sets of data.
How Do LDAP & Active Directory Compare?
LDAP is a protocol, but vendors built directories where LDAP was the primary means of communicating with the directory. They were often known as LDAP servers.
The servers were mainly used as an information store about users for an application. As a result, they are sometimes compared with Active Directory. This led to some confusion, with people asking which is better: an LDAP server or Active Directory?
There isn’t really a good answer to this question, as it’s not a fair comparison. People might really be asking a different kind of question. For example, is Active Directory a better choice for an application directory than using Ping Identity Directory or Oracle Internet Directory?
Typically, LDAP servers are appropriate for very large-scale applications, such as the millions of subscriber queries made in a wireless telecommunications platform.
LDAP is also good in situations where you have a large number of user authentications taking place. At one point, Twitter had a very large LDAP service powering its user authentication.
Due to its design, Active Directory is not ideal for very large-scale implementations with a single community of users. It does scale very well when the organization is distributed into multiple forests and domains.
There are Active Directory implementations with hundreds of thousands of users, but they are all managed in localized domains and forests.
Where Active Directory Excels
Active Directory is excellent at its core job, which is managing access to on-premises Microsoft-based technology, such as Windows clients, servers, and SharePoint/Exchange.
Group policy in Active Directory can be very effective at securing Windows computers due to the tight integration between domain-joined Windows computers and Active Directory. LDAP servers have no equivalent here.
Which Is Right for Your Business?
At Okta, we support both Active Directory and LDAP environments. The distinct benefits of each work better for certain businesses.
Many of our customers have both Active Directory and LDAP servers in their organization. We are able to connect to both and unify the information into the Okta Universal Directory.
References
Active Directory Domain Services Overview. (May 2017). Microsoft.
Understanding Active Directory. (March 2018). Medium.
What Is Kerberos Authentication? (October 2009). Microsoft.
Configuring Active Directory for LDAP Authentication. IBM.
Active Directory Domain Services Overview. (May 2017). Microsoft.
Understanding Active Directory. (March 2018). Medium.
North Korean Hackers May Be Dabbing in Ransomware Again. (July 2020). PC Magazine.
Report Finds Serious Flaws in COVID-19 Vaccine Developers' Systems. (July 2020). xTelligent Healthcare Media.
LDAP and Active Directory. Active Directory 360.
