In 2024, Verizon reported that 45% of data breaches in a recent year involved the use of stolen credentials. At the same time, 90% of identity stakeholders said incidents
directly impacted their business. With the costs of security breaches exceeding $4.8 million at the latest estimate, the need to securely manage identities is greater than ever.
Problems with disparate identity governance and administration solutions
Disparate identity governance and administration (IGA) solutions cause several problems:
- Operational Inefficiencies: Since access management is not part of the solution, manual integration is required.
- Inconsistent policies: The IGA and access management solutions use different models that have to be reconciled and managed by security teams.
- Lack of visibility: Separation from access management causes blind spots between identity and access.
- Poor user experience: Synchronization between IGA and access management results in delays or errors that affect user access.
- Less auditability: Disparate event logging systems make reconciliation difficult.
- Security vulnerabilities: Duplication of identities and policies between systems increases the attack surface and reduces security.
As a result, disconnected IGA solutions fail to meet the security and productivity goals they were meant to address.
What is identity and access management?
Identity and access management (IAM) is a cybersecurity framework that controls user access to digital resources. IAM systems use policies, processes, and technologies to:
- Help ensure that users have the right permissions to do their jobs
- Protect sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access
- Streamline and automate user management
- Improve security and user experience
- Enable better business outcomes
How does access management work?
Access management solutions authenticate users and deliver access to authorized applications via single sign-on (SSO). The user’s access to applications will be provisioned first and governed by the IGA solution. The access management solution requires a directory or database for users and their application identities, policies that control access, and connectors to applications.
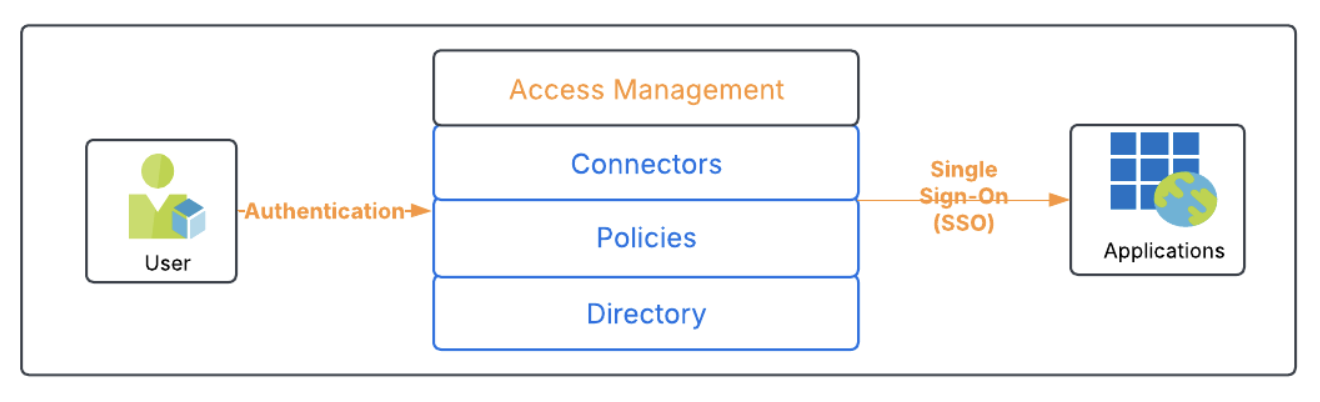
What is IGA?
Identity governance and administration (IGA) is a solution for identity lifecycle management and to govern or attest to users' identities and entitlements across computing environments, e.g., applications and systems.
How does IGA work?
To achieve this, IGA solutions typically include features like user provisioning, e.g. for joiner/mover/leaver (JML) operations, and correlating users from authoritative sources such as human resources (HR) systems to their respective digital identities. IGA solutions also include key capabilities like self-service access requests, entitlement management, and access certifications (a.k.a. user access reviews)
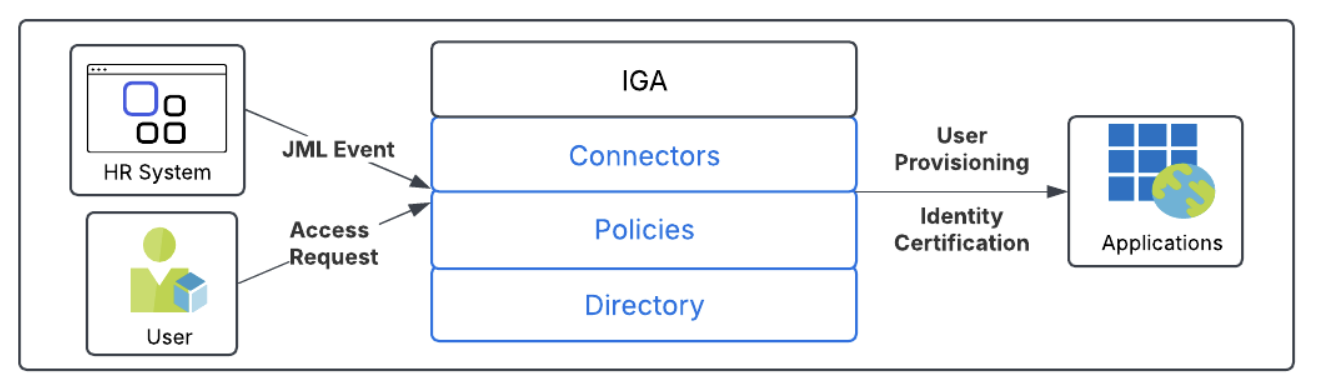
Description of the IGA stack:
- A directory, which contains the user information from the HR system, the user’s identities on the systems and applications, and other information
- Policies, which map users to application identities, authorizing users to applications
- Connectors, programs that communicate with the user sources and identity stores
- IGA performs these key operations:
- User provisioning operations based on JML events that are initiated by the user source system
- User provisioning operations based on approved access requests
- Identity certification based on a schedule or in response to JML events
Standalone IGA solutions typically lack features like SSOn and multi-factor authentication, which are usually included in Identity Access Management solutions.
Overlap between access management and IGA
When compared side-by-side, it’s clear that standalone IGA and access management solutions have some common services.
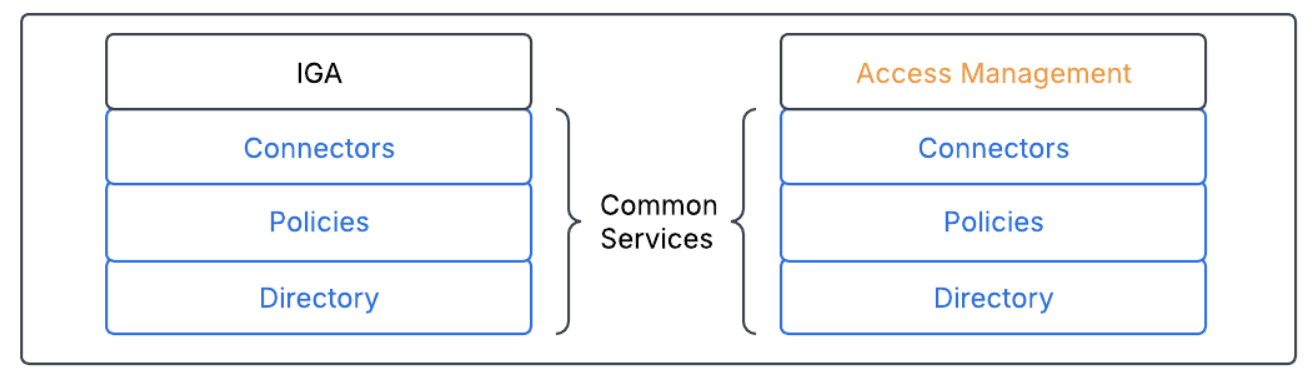
Both solutions require a directory or database, policies for controlling which users have appropriate levels of access to systems, applications, and connectors for performing identity operations on those systems and applications.
For example, the IGA solution is managing a user, Morgan Smith. The IGA solution provisions the identity as M.Smith@yourmail.com to a SaaS application. The access management solution must use the same identity to SSO the user to the SaaS application.
The model
The disparate model of IGA is used when the IGA solution doesn't use the services that are part of the access management solution, as depicted below.
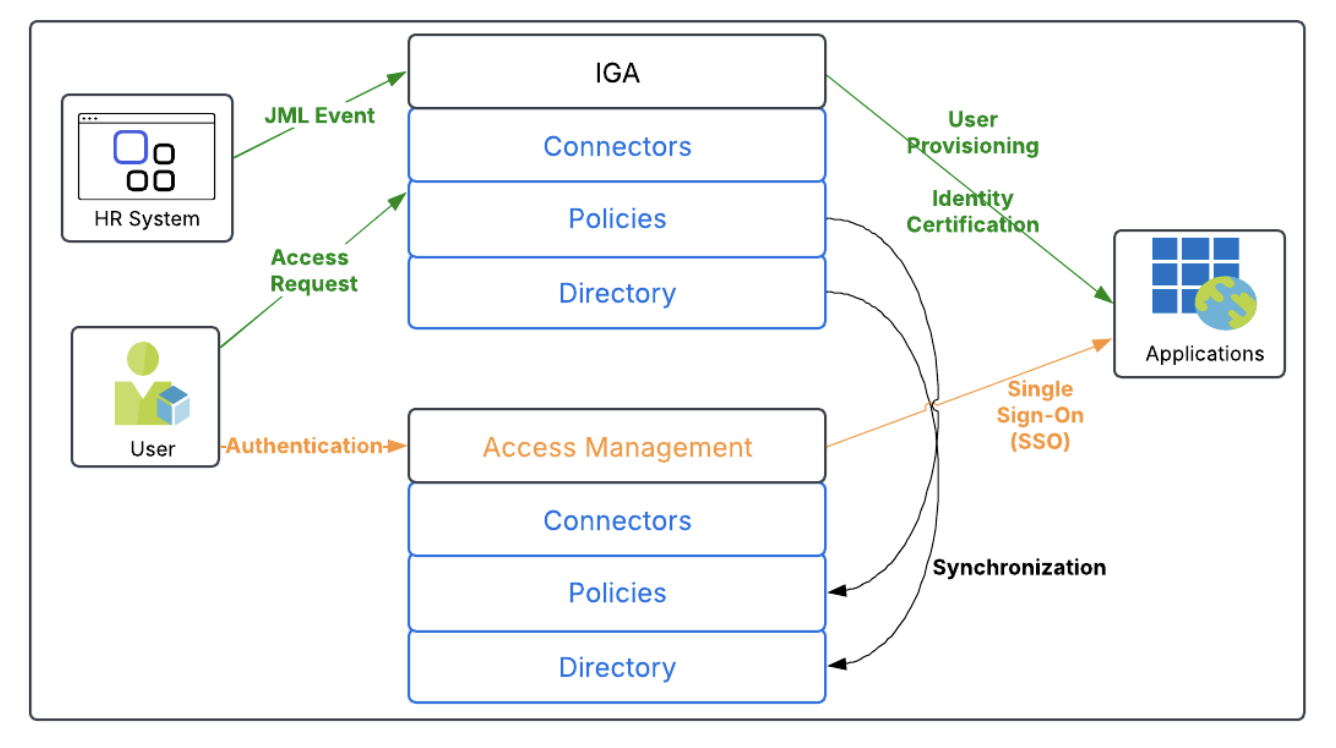
Several important differences and complications exist between the disparate model and the converged model.
- As there are no common services in the disparate model, the access management solution and IGA solution must be administered separately.
- The identities provisioned in the IGA solution must be duplicated in the access management solution.
- Policies regarding which users have access to which applications must be synchronized from the IGA system to the access management system
- The IGA solution connectors aren’t shared with the access management solution, so each solution must be integrated with the managed applications separately.
What is a converged IGA solution?
The converged model for IGA uses components and services that are shared with the access management components of the IAM stack. This results in benefits such as:
- Single platform for governance provisioning, access request certifications, and workflows
- Seamless integration of HR systems, apps, and infrastructure
- Identity as a central control panel for security and productivity
An example of this model is depicted below.
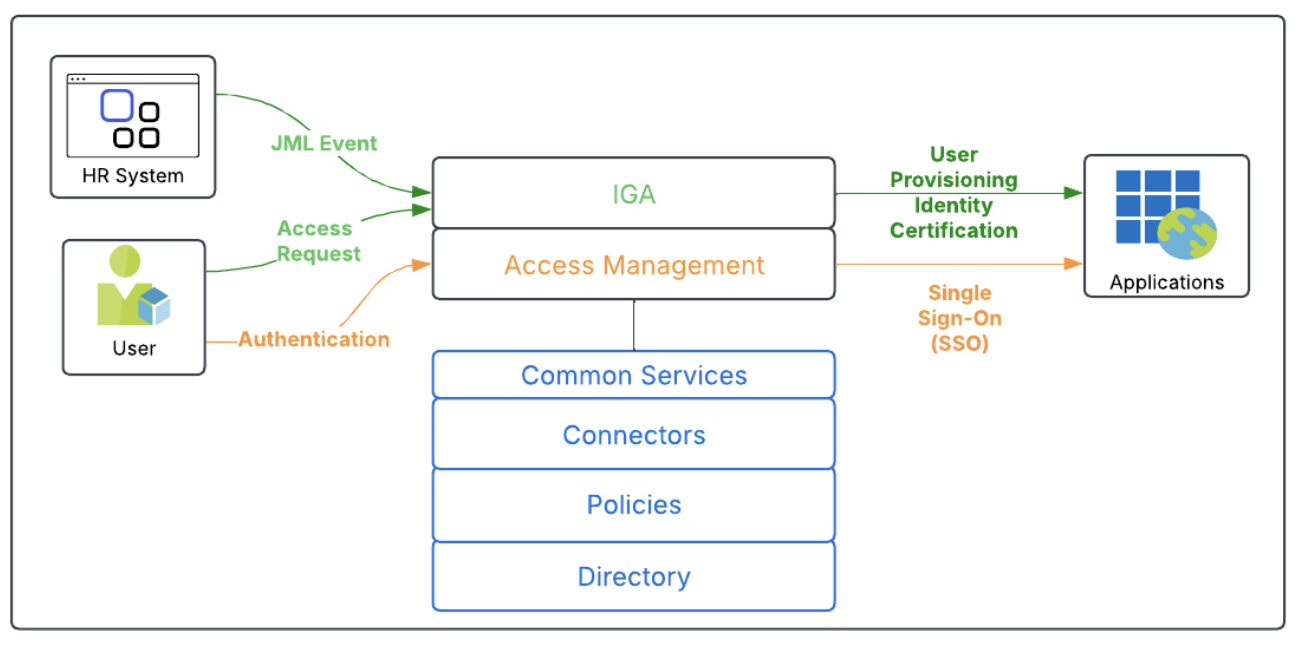
Using this model, common components, including the directory and policies, are used by both the IGA and access management solutions. Only a single connection to the source of users ( e.g., the HR system) is required. No orchestration is required between IGA and the access management components because both solutions use common services.
Advantages of the converged IGA model
The converged model of IGA has several advantages over the disparate model of IGA.
- Faster time-to-value: Reduce complexity of deploying and maintaining both solutions. Improved user experience: Reduce latency in users gaining access during JML operations.
- Unified visibility and control: The use of a separate stack of components in the disparate model increases the attack surface for both of the IAM components, which increases security risks
- Consistent policies across environments: The converged model simplifies managing access, which reduces errors and improves reliability.
- Stronger security posture: This reduces the risk of over-provisioning and orphaned accounts.
- Automation: This streamlines certifications and audit readiness
- Scalability: This makes the model easier to grow with the business and adapt to changes.
How to get started with a converged approach
- Key capabilities to consider when evaluating a converged IGA solution
- Look for platforms that deliver integrated IGA, access management, and automation.
- Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), including ease of deployment, time to value, and ongoing maintenance
- Consider future needs and use cases, including a hybrid cloud, application sprawl, and a growing workforce.
In a world where identity is security, convergence isn't a nice-to-have; it's a must. Disparate IGA tools create complexity, impact productivity and threaten security. A converged IGA solution offers unified policies, centralized visibility, and automated workflows, which results in a better experience for admins and end users, plus a lower TCO and better security. Organizations may also find that a converged solution results in lower licensing costs.
Take a moment to evaluate your stack:
- Are your governance, provisioning, and access controls scattered across multiple tools?
- How quickly can you prove compliance or respond to access risks?
- Is your team spending more time managing tools than enabling the business?
If any of these questions raise flags, it might be time to explore a converged IGA approach. Okta’s unified approach to Identity is based on the converged IAM model described above, which results in lower TCO and greater security. Okta’s IGA solution (Okta Identity Governance) relies on the same components as Okta’s access management solutions. To learn more about Okta’s solution for IGA, please see the links below.
https://www.okta.com/products/identity-governance/
https://help.okta.com/en-us/content/topics/identity-governance/iga-overview.htm






