CIO eGuide: Preventing Data Breaches
Executive Summary
Data is becoming increasingly important in business. As a result, more and more organizations are becoming attractive targets for hackers. Data breaches caused by stolen credentials are on the rise. You need smarter tools to protect your organization against the monetary and reputational damage caused by a data breach. This guide will explain how Okta Adaptive Multifactor Authentication (MFA) provides the security that IT needs, while also providing the simplicity end users want.
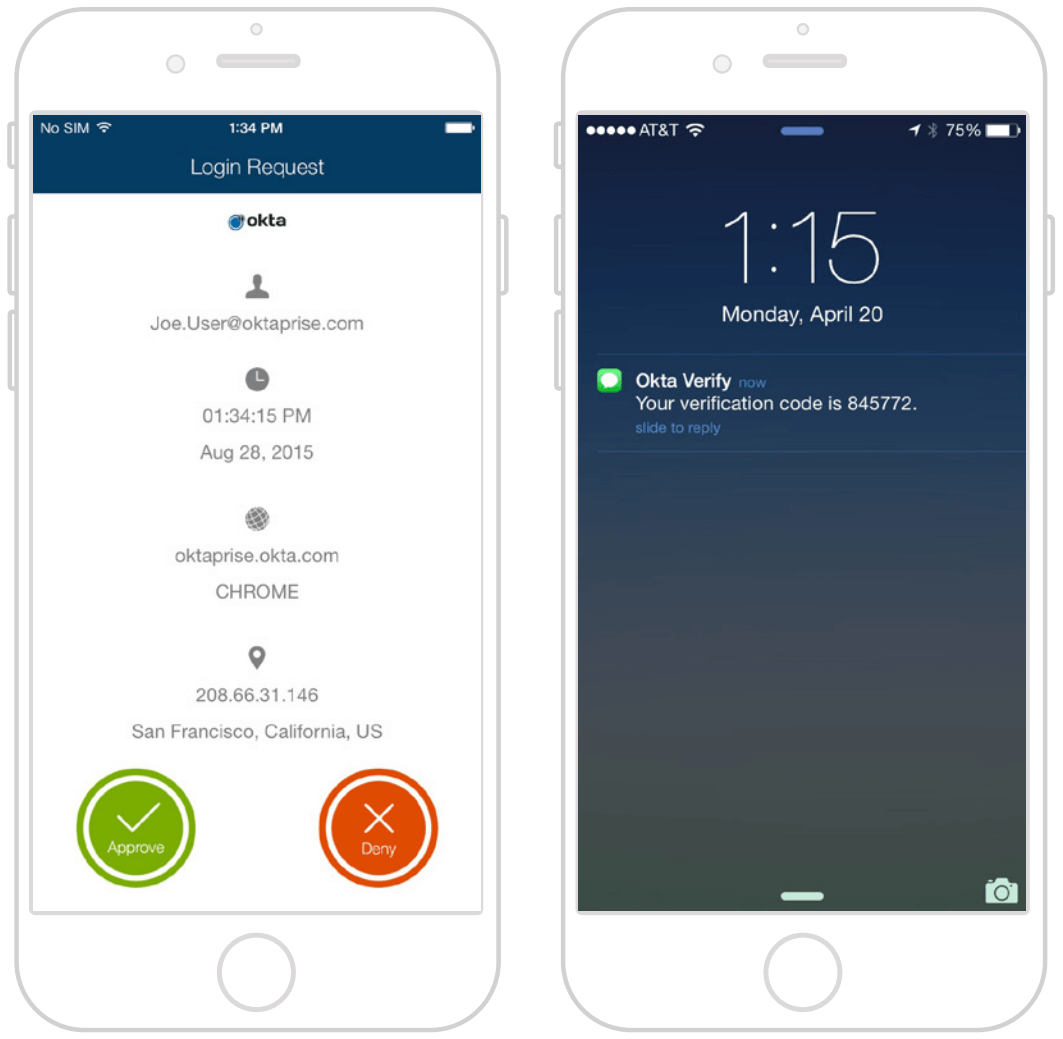
The Challenge of Authentication Security
IT and security professionals have long known that multifactor authentication is an effective way to secure critical applications and infrastructure against unauthorized access. The challenges are that managing MFA products is expensive for IT, and repeatedly entering passcodes is frustrating for end users. As a result, many organizations have been deterred from deploying MFA beyond a select group of IT and privileged users.
Every time your organization launches a new application or product, securing it with MFA requires a timeconsuming integration project. Many organizations struggle to keep track of which apps and infrastructure are secured with MFA, creating security holes and coverage gaps that put the organization at risk. In addition, both IT and end users are familiar with the shortcomings of the hardware tokens that many traditional MFA solutions use for verification. These tokens are time-consuming to manage, easy to lose, and expensive to replace.
In an effort to provide a less irritating user experience, some organizations have tried security questions as a less-burdensome alternative. However, social networks and social engineering have made it easy to find the answers to many common security questions. As a result, security questions are not typically secure enough for sensitive applications. These questions are not necessarily easier for users either. Many users often forget the answers to their own security questions.
Security Done Smarter
You need better tools to protect your applications and data from the skilled thieves hoping to profit from it. Okta Adaptive MFA is that comprehensive and simple authentication solution you have been looking for. It allows you to manage access based on contextual access policies. It supports a rich set of modern factors. It will be capable of leveraging big-data insights gleaned from millions of users, devices, and authentications. And it integrates easily with the applications and network infrastructure you are trying to protect.
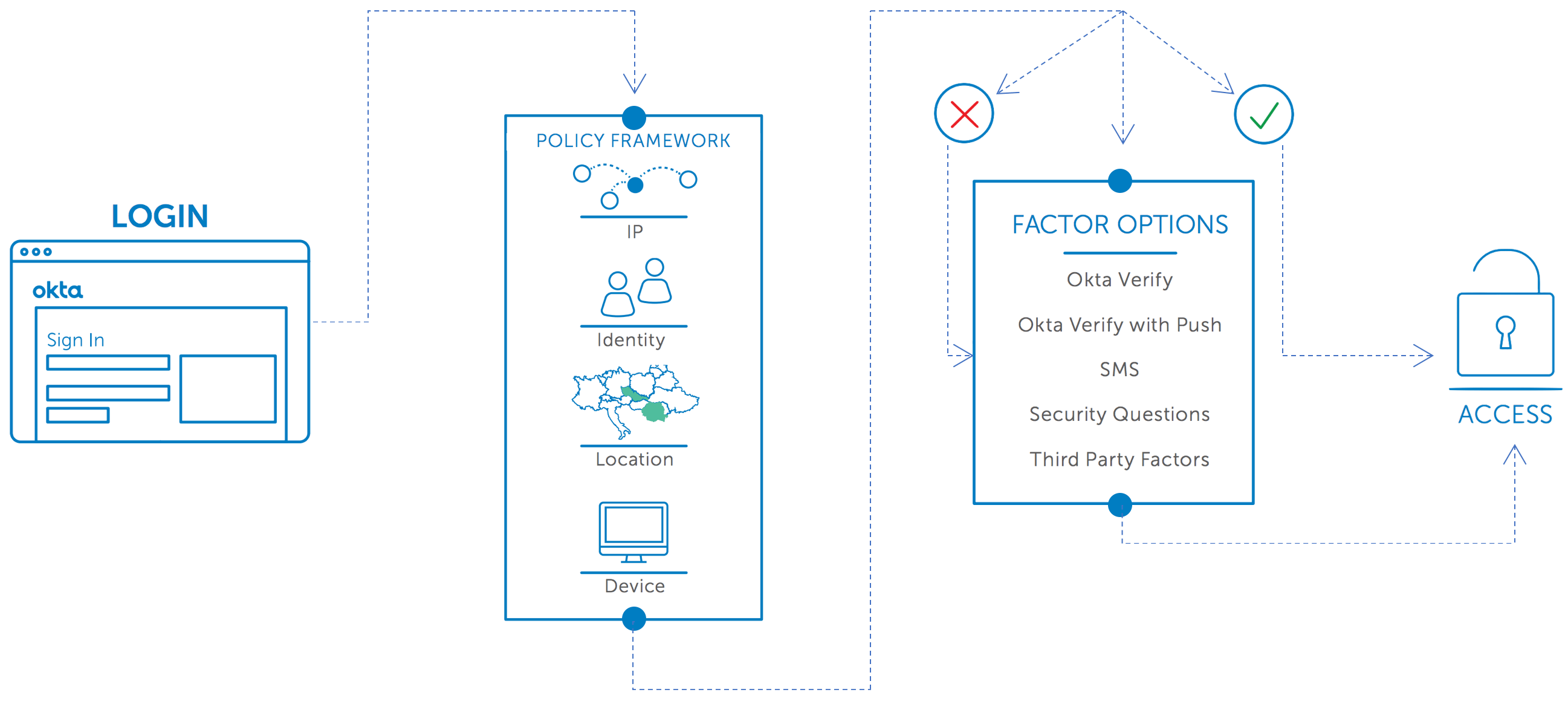
Reduced Risk with Contextual Access Management
Contextual access management helps you reduce risk by examining when, where, and how your users try to access your applications and data. Based on detailed intelligence about who and where your users are, you can choose to allow access, require step-up authentication, completely deny access, or soon even restrict the scope of a user’s access to certain applications. These decisions are based not just on passwords, security questions, and tokens but on who the user is, what network or country they are connecting from, and what device they are using to connect.
Okta Adaptive MFA’s granular contextual access policies let you secure more resources with little or no impact on your users. They are only prompted for verification when necessary, not every time they access your site or tools.
Comprehensive User Coverage Through a Modern Set of Second Factors
You can stop worrying if your security policies will fail because not all users have the latest smartphone, or because they are located abroad, or because users will have no access to a phone at all. Okta Adaptive MFA can secure access for all types of users in all sorts of circumstances. Users with smartphones can take advantage of Okta Verify with Push, while users without smartphones can use alternative methods, such as SMS, or third-party factors like YubiKey.
It is easy to migrate users from their current hardware tokens to Okta Verify with Push with flexible policies that enable users to set up new factors without breaking your current solution. Okta’s enrollment policies let you choose which factors are required and which are optional for users based on the user’s group memberships, also ensuring users configure redundant factors to reduce IT support costs.
Security that Adapts to Risk
How much time do you waste reacting to false positives? A modern authentication tool—capable of tapping big data to make decisions—is too smart for that. Get back to work. Let Okta’s insight into millions of users, devices, and authentication requests identify possible attacks on your applications and prevent unauthorized access without distracting you. Stand-alone MFA solutions see only part of the picture. But Okta Adaptive MFA will process single-sign-on and enterprise mobility management data at lightning speed to make smart decisions in real time. The combination of user, device, and behavioral context does more than reduce the noise of false positives. It increases security. Hackers simply aren’t capable of spoofing all the signals Okta Adaptive MFA examines to build a user profile.
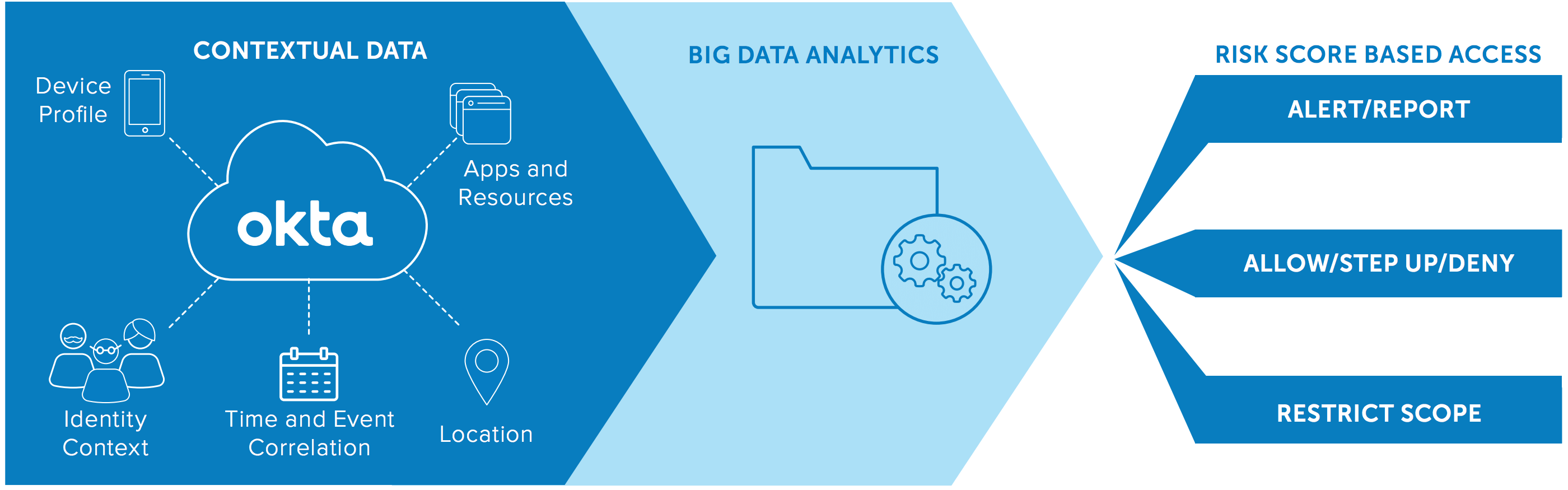
More importantly, Okta Adaptive MFA will do more than generate alerts. Okta controls access to your applications centrally. So when it detects an abnormal request, it stops the potential hacker automatically. Your risk is quickly and effectively reduced.
Fast Deployment from the Cloud
Okta’s 100% cloud-based adaptive MFA solution easily and quickly deploys security to all your applications and critical infrastructure. Adding new integrations is easy—and secure. Choose from the 500+ SAML and RADIUS-enabled applications and VPNs in the Okta Application Network (OAN). Because you manage your users, devices, and MFA security policies from one central hub, you completely eliminate the coverage gaps that historically occurred when you add, change, or remove resources and users. Your new products will be up and running—securely—in record time.
Conclusion
IT can easily deploy effective security controls with Okta Adaptive MFA while users get an easier log-in experience. Okta Adaptive MFA is smarter. So it makes your job simpler. It lets you free up IT staff time—even while migrating from your existing on-prem MFA solution, or adding new applications and users—while maintaining a continuous, secure guard over access to your apps and infrastructure.