Okta Directory Integration - An Architecture Overview
For most companies, Active Directory (AD) or LDAP plays the central role in coordinating identity and access management policies. Directory integration typically serves as a "source of truth" for user identities, and it provides access control to on-premises resources such as networks, file servers, and web applications. A byproduct of the transition to cloud applications is the proliferation of separate user stores; each cloud application typically is rolled out independently and therefore has its own unique database of user credentials.
Okta's cloud-based identity and access management service solves these problems with a single integration point that provides a highly available solution for all cloud and web-based applications Active Directory integrations.
Read this whitepaper to learn how Okta eliminates the pitfalls that come with trying to build and manage multiple on-premises active directory integrations yourself.
User Directories and the Cloud: An Overview
For most companies, Microsoft Active Directory (AD) or Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directories such as SunOne or Oracle Internet Directory play the central role in coordinating identity and access management policies. AD/ LDAP typically serves as a “source of truth” for user identities and provides access control to on-premises resources such as networks, file servers, and web applications (see Figure 1). When on-premises applications are integrated to Active Directory or LDAP, users get the best possible experience: they log in to their domain once and are granted access to the appropriate resources. Administrators benefit too—they maintain clear control over who has access to what. This model is ubiquitous because it works well with LAN-based architectures (where applications are served from hardware inside the firewall). But as we’ll show, this approach begins to break down as enterprises shift to cloud-based applications, and a new solution is needed.
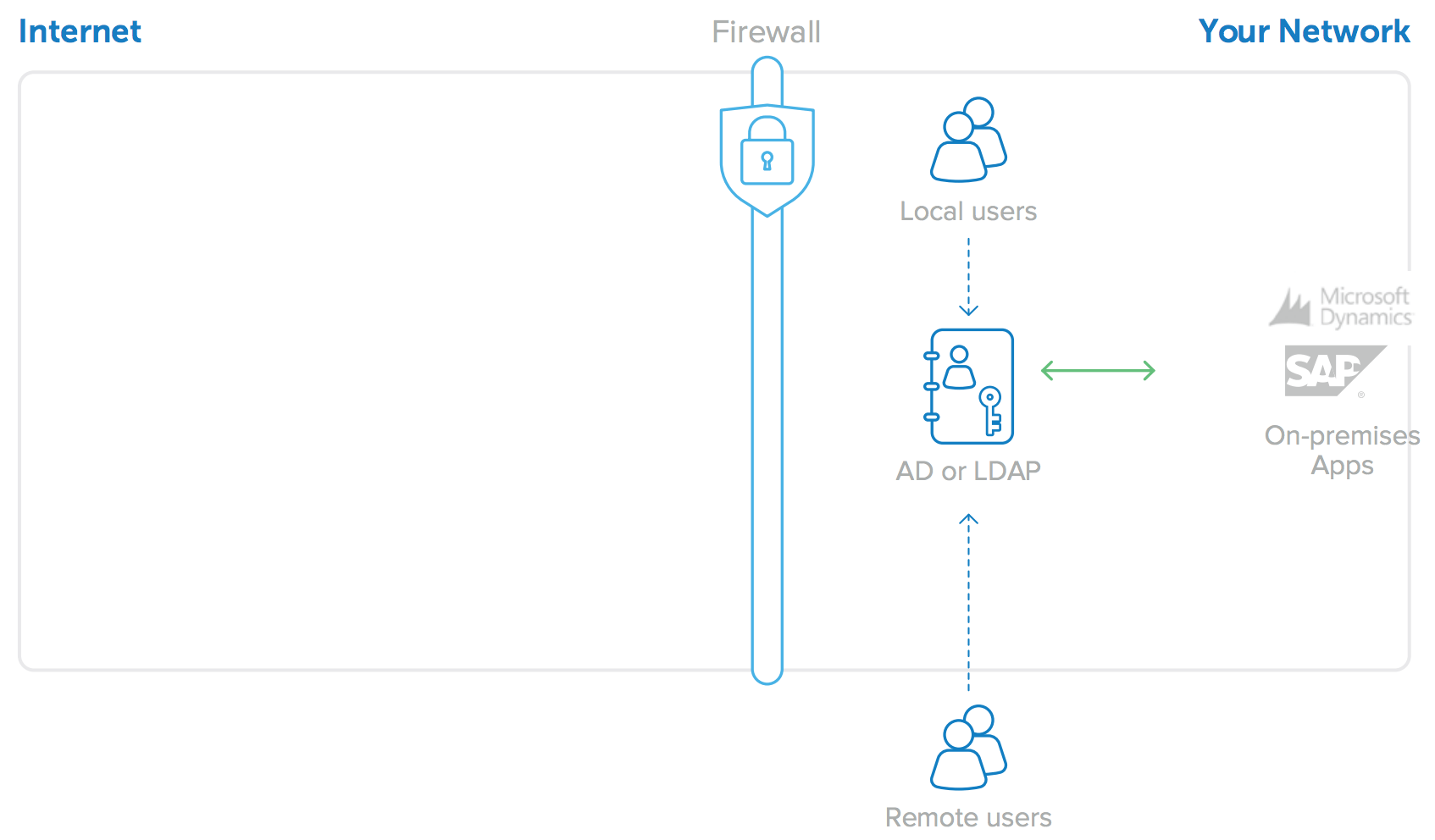
Figure 1: AD or LDAP for on-premises application user identities
A byproduct of the transition to cloud applications is the proliferation of separate user stores; each cloud application typically is rolled out independently and therefore has its own unique database of user credentials (see Figure 2). This is a minor nuisance with only one or two applications, but as companies adopt more and more cloud applications, administrators are faced with an unmanageable number of different user directories. And this problem is only getting bigger. Users’ passwords proliferate with each new application, and administrators quickly lose control over who has access to what. Worse still, when an employee leaves, most companies cannot easily and accurately identify which accounts to deactivate, nor do they have any auditing capabilities to ensure the necessary deprovisioning occurs in a timely manner.
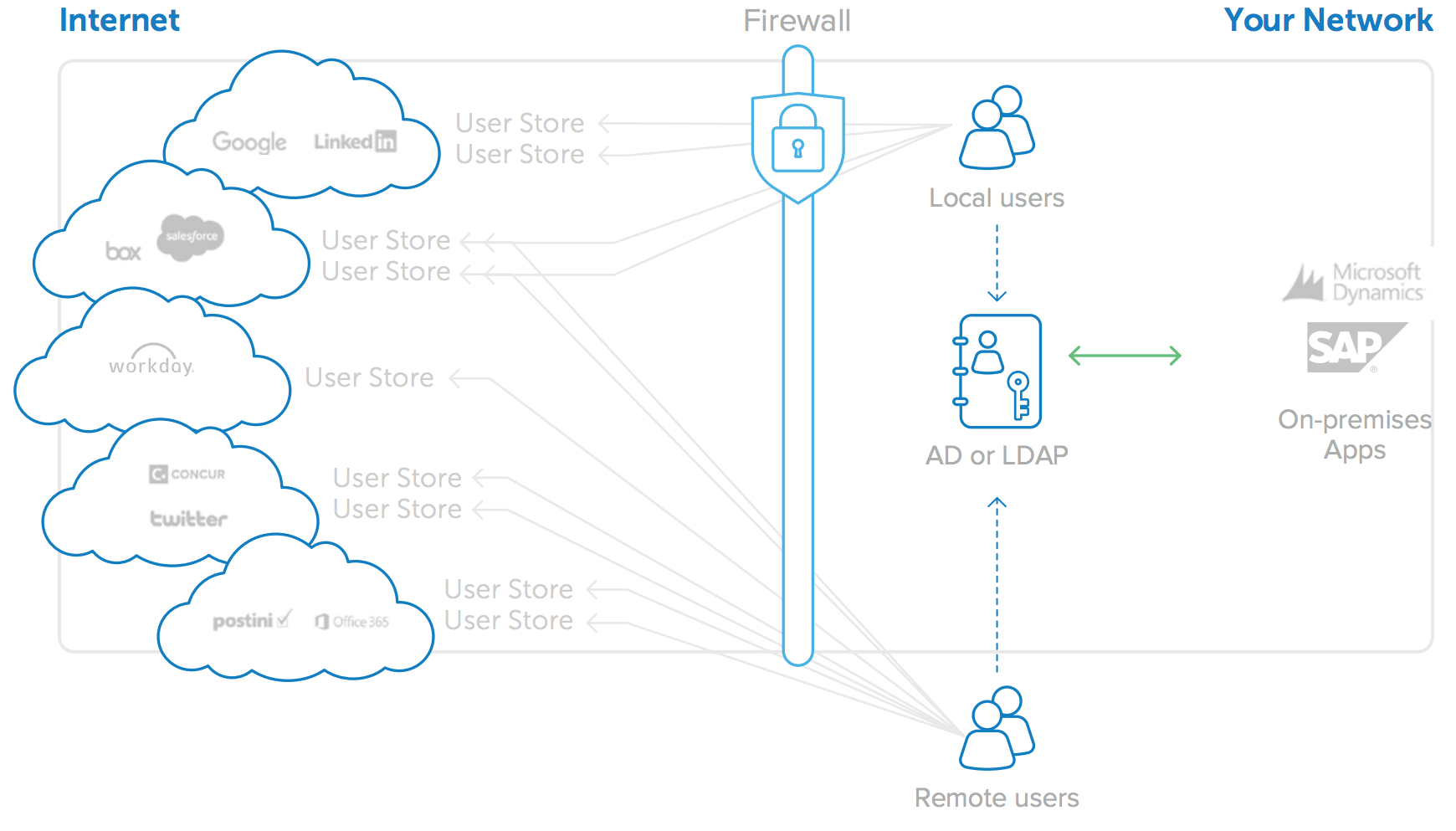
Figure 2: Adoption of cloud applications leads to proliferation of user stores
One solution to the problem of independent user store proliferation is to attempt to integrate all cloud applications to a single, shared identity store (see Figure 3). Active Directory or LDAP user stores are by far the most convenient options for this, as they can provide identity management for both on-premises and cloud-based applications. Some cloud application vendors provide APIs or toolkits that allow enterprises to try to connect the application’s standalone identity stores to AD or LDAP. However, integration via APIs requires custom development, and each of the toolkits is different and can often require significant investment in setup, equipment (hardware to run the connector software),and maintenance as the applications change over time. As the number of cloud applications increases, this model of per-app AD or LDAP integrations becomes prohibitively expensive. There is always the next new application that the business needs to run.
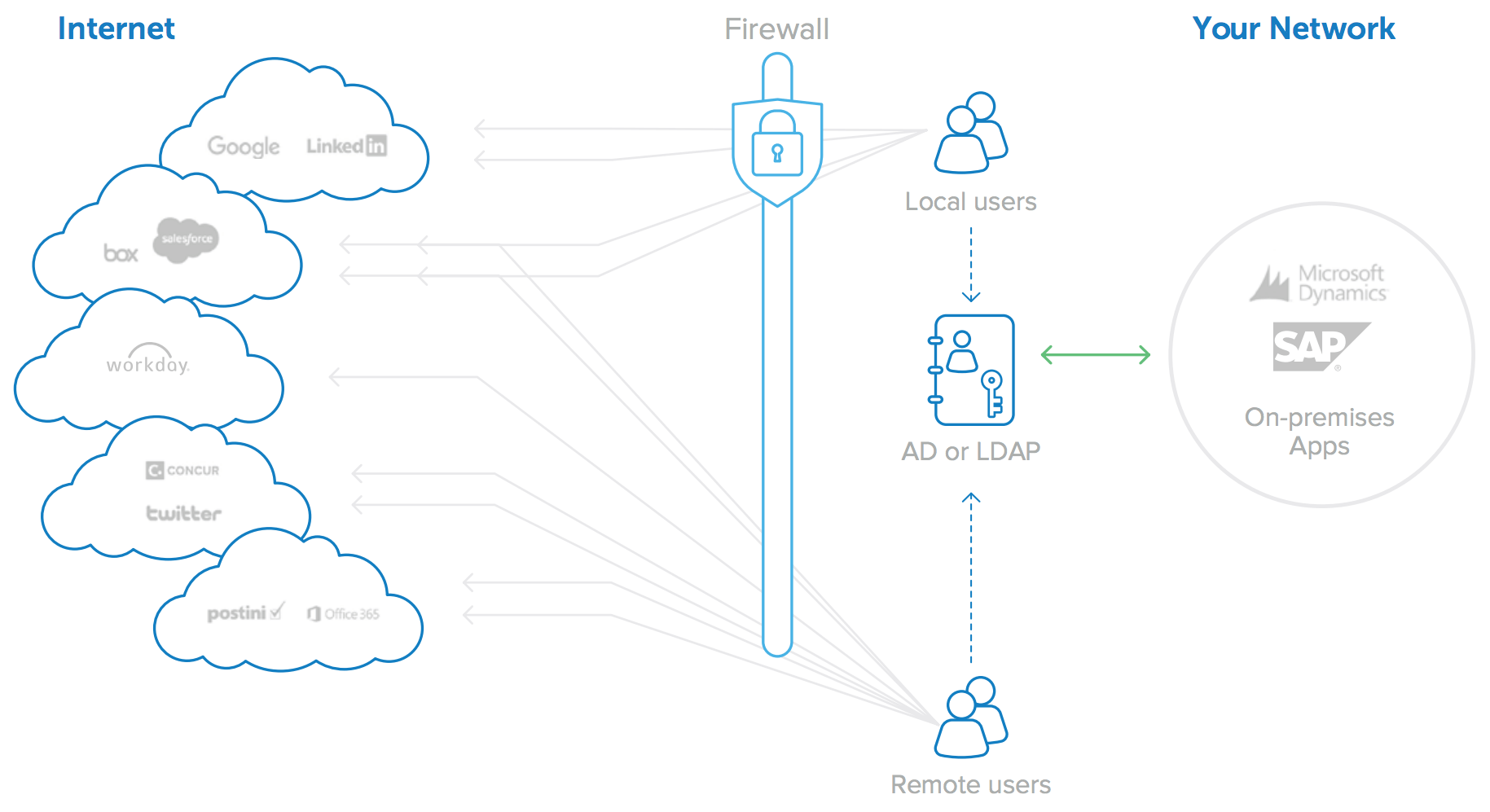
Figure 3: Integrating with multiple cloud applications is costly and difficult to maintain
Okta’s cloud-based identity and access management service solves these problems with a single integration point that provides a highly available solution for all cloud and web-based application AD and LDAP integrations.
Okta eliminates the pitfalls that come with trying to build and manage multiple on-premises directory integrations yourself:
Pitfall of DIY AD/LDAP integrations |
Okta's Approach |
|
Do you have the correct skillset to develop these integrations? |
With Okta, integrations do not require programming or development experience and can be accomplished in minutes through our easy-to-use interface |
|
How will you upgrade and maintain integrations? |
Okta works with ISVs and monitors changes and upgrades to existing APIs to take advantage of the latest functionality; we release updates weekly to reflect changes. |
|
How do you monitor the health of the integration? |
Okta continuously monitors and tests existing integrations to ensure that the integration functions as expected after upgrades and releases. |
|
Which protocol will you use to connect to each cloud application? |
Okta eliminates the need to know SAML, OAuth, SCIM, and numerous other integration protocols, because Okta manages these integrations for you. |
|
What happens when the server running your home-grown, toolkit-based integration fails? |
Okta automatically enables failover recovery with a redundant-agent architecture. |
|
How will you integrate your cloud app with a multiple domain AD or LDAP configuration? |
Okta has built-in support for multiple AD and/or LDAP domain environments. |
|
What firewall changes are needed for each cloud app-to-AD/LDAP integration?
|
With Okta, there are no firewall changes needed to support AD or LDAP integration.
|
Once in place, Okta provides an infrastructure that allows companies to freely pursue new cloud applications while still leveraging internal directories for their employee user identities. This allows users to access any cloud app using their existing AD or LDAP credentials; it enables IT admins to control access to those applications from a single control panel; and it combines AD or LDAP security groups with individual user assignments.
Okta Directory Integration for All Your Cloud Apps
Okta offers a complete and easy-to-use directory integration solution for cloud and on-premises web applications. The Okta on-demand Identity and Access Management service provides user authentication, user provisioning and de-provisioning, and detailed analytics and reporting of application usage, for both cloud applications and on-premises web applications. A key component of this service is Okta’s directory integration capability, which is very easy to set up and is architected for high availability. In addition, Okta maintains the integrations for you, with thousands of applications supported in Okta’s Application Network (OAN).
For AD integration, Okta provides three lightweight and secure onpremises components:
• Okta Active Directory Agent: A lightweight agent that can be installed on any Windows Server and is used to connect to on-premises Active Directory for user provisioning, deprovisioning, and authentication requests.
• Okta Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) Web Application: A lightweight web application that is installed on an Internet Information Services (IIS) and is used to authenticate domain users via Integrated Windows Authentication.
• Okta Active Directory Password Sync Agent: A lightweight agent installed on your domain controllers that will automatically synchronize AD password changes, send to Okta, and keep your user’s AD passwords in sync with the apps they use.
For LDAP integration, Okta provides a single lightweight and secure on-premises component:
• Okta LDAP Agent: A lightweight agent that can be installed on any Windows Server and is used to connect to on-premises LDAP user stores for provisioning, de-provisioning, and authentication requests.
The Okta AD/LDAP Agents, the Okta IWA Web App and the Okta AD Password Sync Agent combine with the Okta cloud service itself to form a highly available, easy to set up and maintain architecture that supports multiple use cases. This paper provides additional details about this flexible architecture.
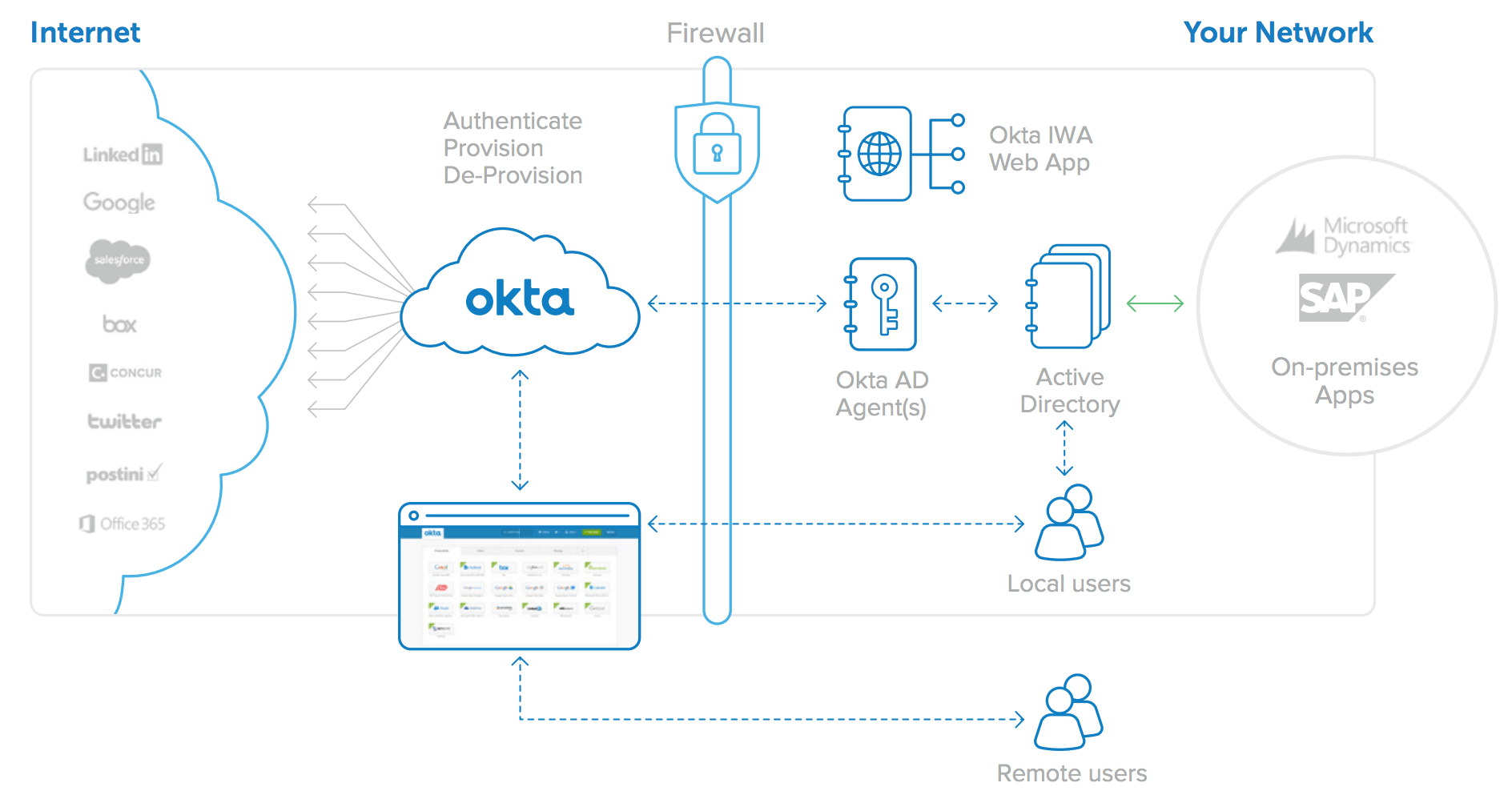
Figure 4: Okta for Active Directory architecture: One integration for all web applications
Okta’s directory Integration offers the following:
• Simple and Secure Setup and Configuration
• Real-time provisioning
• Intelligent user synchronization
• Just-in-time user provisioning
• Robust delegated authentication
• Integrated desktop single sign-on (SSO) (AD only)
• Self service password reset support (AD only)
• Security group-driven provisioning
• Automated one-click deprovisioning
• Single sign-on for directory authenticated apps
Simple and Secure Setup and Configuration
With Okta, enabling directory integration is a simple wizard-driven process. With one click from the Okta administrative console, you can download the Okta Active Directory or LDAP Agent and install it on any Windows Server that has access to your Domain Controller. The Okta Agents run on a separate server from your domain controller.
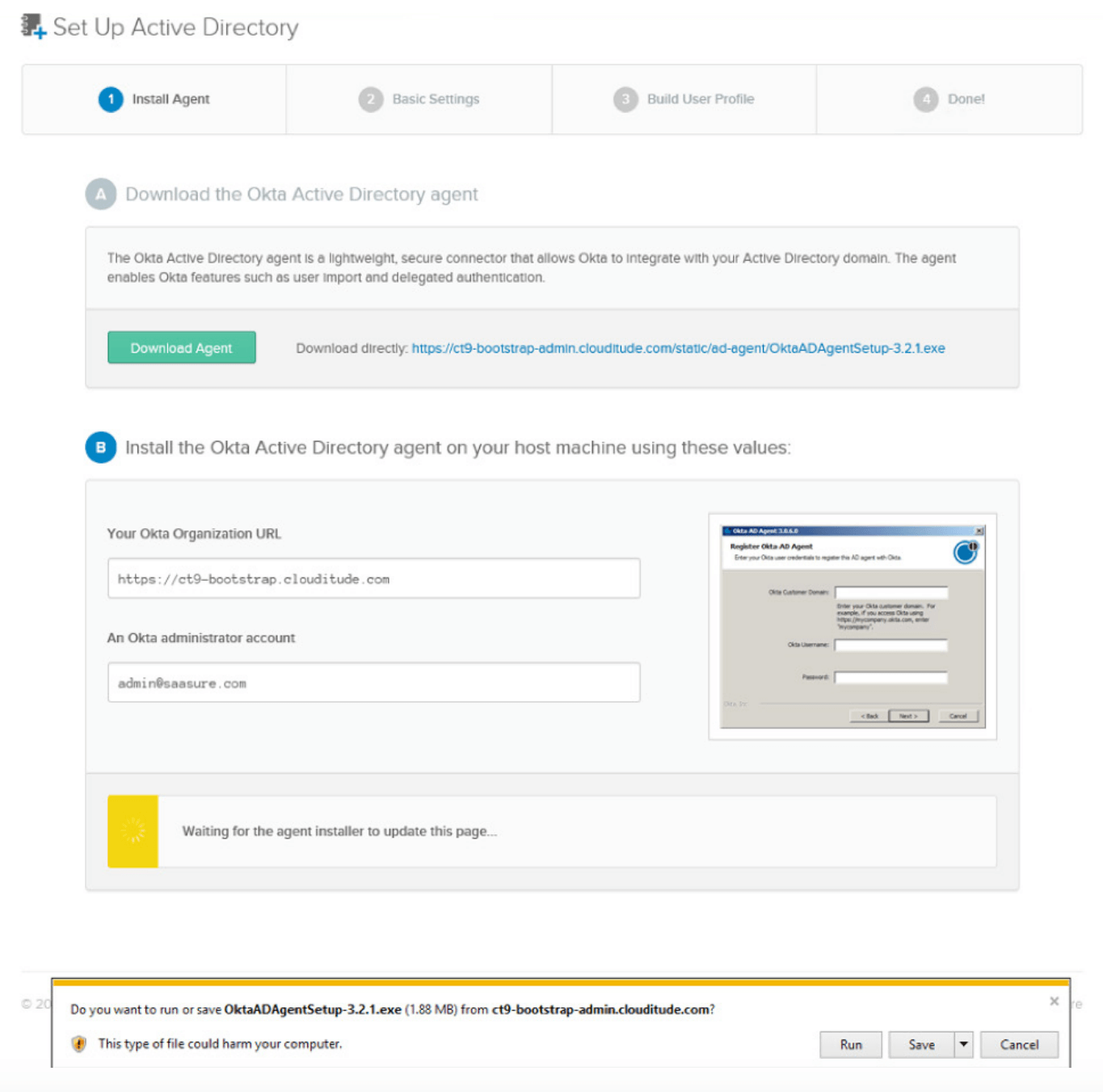
Figure 5: The Active Directory installation process
During installation, you simply enter your Okta URL and AD Administrator credentials and the Okta AD Agent creates a lowprivileged, read-only integration account and then securely establishes a connection with your Okta instance—no network or firewall configuration required.
The Okta AD Agent connects to Okta’s cloud service using an outbound port 443 SSL connection. This connection is cycled every 30 seconds to ensure compatibility with any existing firewalls or other security devices. As a rule of thumb, if a user can log into the host machine using AD credentials and can access the Internet from a browser, the Okta AD Agent will work successfully and will require no firewall changes.
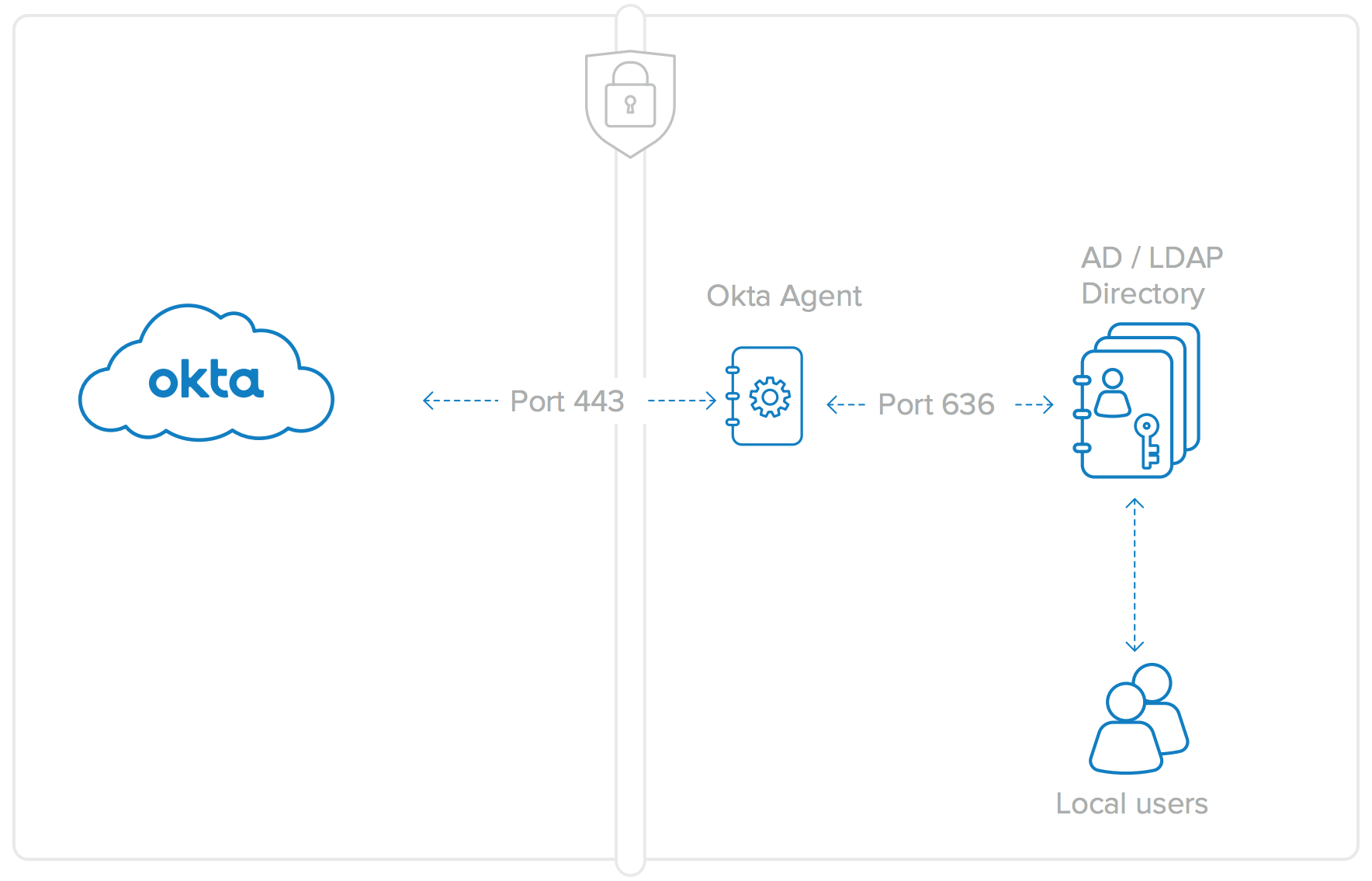
Figure 6: Okta Agent connections are Port 443 for AD (SSL Encrypted) and over Port 636 for LDAP. No firewall changes are needed for either the AD or LDAP Agents.
Communication with the Okta AD/LDAP Agents is secured using SSL and mutual authentication, specifically:
• Okta AD/LDAP Agents to Okta Service: The Agent authenticates the service by validating the Okta server SSL cert for mycompany.okta.com. The service authenticates the Agent using a security token given to the Agent on registration. The registration process requires Okta administrator credentials before generating the security token. The security token is specific to each Agent and can be revoked at any time.
• Okta Agent to the Domain Controller or LDAP server: The Agent authenticates with the Domain Controller using the low-privileged, read-only integration account that was created during the agent install process.
Real Time Synchronization
Companies do not need to worry about inconsistent profile information between their user store and Okta that may occur with schedule imports. With real-time synchronization, Okta seamlessly updates profiles on every login. So whether you change individual profile information or larger group information, your users will be fully updated throughout the day in Okta.
The process to enable real time synchronization is:
1. Download and install the appropriate Agent.
2. Import OUs and Groups (without the member attributes).
3. Configure OU selection and username preference. Note: The schedule import pull down menu will be set to Never.
4. Delegated Authentication, and Just in Time Provisioning (JIT) are turned on by default.
5. Users can immediately JIT in without any previous import and become Okta users.
6. On every delegated authentication or JIT request, Group memberships are imported in addition to the full User profile.
7. Users are fully updated on every login and asynchronously.
Admins can change OUs, user profile and group information in Active Directory and users will be fully updated.
Just-in-Time User Provisioning
User provisioning is very simple and fast with Okta’s just-in-time provisioning. With just-in-time provisioning, IT admins can allow new users to be automatically created in Okta provided they already exist in Active Directory or in an LDAP user store.
IT Admins are not required to run an initial import before activating users, saving time during configuration. Users will be able to immediately sign into Okta by going to their login page and signing in with their directory (AD or LDAP) credentials. Administrators will be able to see the full user profile, groups, and group memberships display in the People tab.
The process for just-in-time provisioning is:
1. A user who previously was not provisioned in the Okta service attempts to log in to mycompany.okta.com.
2. Okta and the Okta Agent check the user credentials against Active Directory or LDAP.
3. If the user is active in AD/LDAP, a new user account is automatically created in Okta. The new user account leverages their existing AD credentials.
4. Depending on their directory security group attributes, the user is automatically provisioned to downstream cloud and web applications via the Okta service.
Just-in-time provisioning allows IT admins to increase user adoption of both the Okta service and of all assigned cloud applications, while leveraging the AD or LDAP credentials that their users already know.
Simple-to-Use Delegated Authentication
Okta’s directory integration support also allows you to delegate the authentication of users into Okta to your on-premises AD or LDAP Domain instead. That is, user login attempts to mycompany. okta.com will be checked against Active Directory or LDAP for authentication. Users can then easily log into Okta using their Okta user name and directory password.
More specifically, the process is:
1. The user types his user name and password into the Okta user home page. This login page is protected with SSL and a security image to prevent phishing; multi-factor authentication (extra security question or smartphone soft token) can be enabled as well.
2. The user name and password are transmitted to an Okta Directory Agent running behind the firewall over the SSL connection that had been previously established during setup.
3. The Okta Directory Agent passes those credentials to the AD or LDAP Domain Controller for authentication.
4. The Domain Controller responds with a yes/no answer, validating the user name and password.
5. The yes/no response is transmitted back to the Okta service by the Okta Directory Agent. If yes, the user is authenticated and sent to his Okta My Applications user home page.
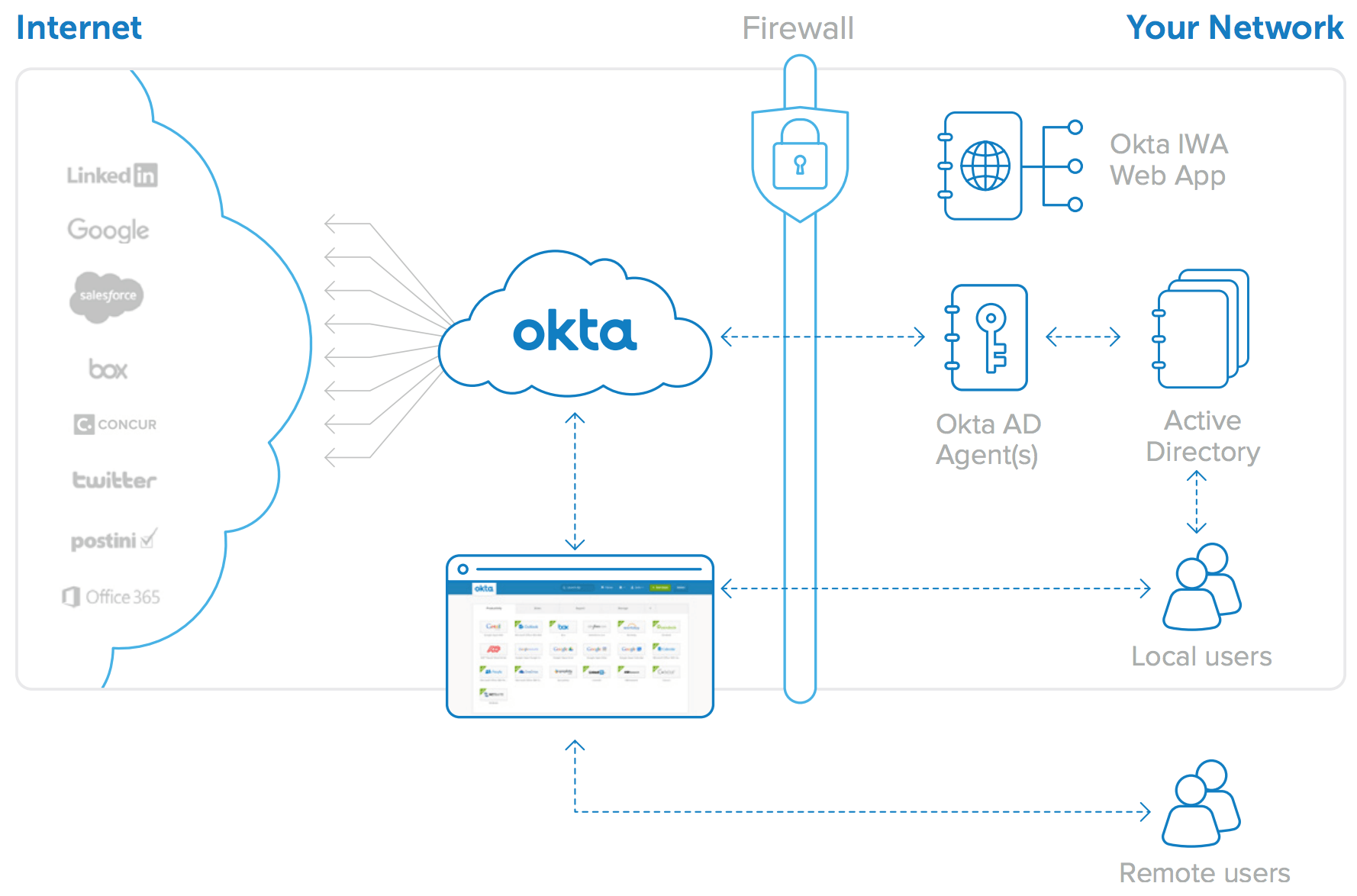
Figure 7: Delegated authentication to Active Directory
The user experience for Delegated Authentication to AD /LDAP is simple:
1. Log in to Okta home page; launch app
2. Okta looks to a directory to authenticate users
3. If valid, Okta SSOs in to cloud apps
Because this feature governs user access into Okta, the architecture supports multiple Okta AD and/or LDAP Agents running in your environment to provide redundancy. If one of the Okta AD or LDAP Agents stops running or loses network connectivity, the authentication requests are automatically routed to the other Okta AD or LDAP Agents.
With this authentication mechanism, the user’s password is never stored in the Okta service and your directory is maintained as the immediate and ultimate source for credential validation. Because AD or LDAP is always relied upon for user authentication, changes to the user’s status (such as password changes or deactivations) are reflected immediately in the Okta service.
Desktop Single Sign-On
Okta supports Desktop Single Sign-On, extending local users’ Windows domain login procedures to grant access to Okta and to their cloud applications. Okta’s AD integration uses Microsoft’s Integrated Windows Authentication to seamlessly authenticate users to Okta that are already authenticated via their Windows domain login. You simply download and install Okta’s IWA web application, configure the relevant IP ranges, and the setup is complete.

Figure 8: Desktop SSO with Okta IWA web application
The behind-the-scenes steps that enable seamless login to the Okta service via Desktop Single Sign-On (shown in Figure 9) are:
1. User navigates to https://mycompany.okta.com.
2. The user is redirected to the locally installed IWA web application.
3. The IWA web application transparently authenticates the user via Integrated Windows Authentication (Kerberos).
4. The user is redirected back to the Okta login page with cryptographically signed assertions containing his AD user identity.
5. The Okta service validates the signed assertions and sends the user directly to his Okta home page.
Note that all of the above steps are transparent to the user. The user experience is simple: navigate to https://mycompany.okta.com and then land immediately on the user home page containing links to all of his assigned applications. Alternatively, a user can simply click a link corresponding to a particular application and then be automatically signed in to that application. The authentication to AD behind the scenes is transparent to the user.
Lastly, remote users or users out of the office continue to find and SSO into all of their cloud applications by simply visiting the Okta user home page.
Self Service Password Reset Support
Your users can also change their Active Directory password via Okta. When a user’s AD password expires or is reset they will automatically be prompted to change it the next time they log in to Okta. Users can also proactively change their AD password directly from the account tab on their Okta homepage, and Okta keeps all of these credentials synchronized with AD.
Security Group–Driven Provisioning
Okta’s service has a group feature that can be used to drive bulk application provisioning and assignments to Okta users according to what groups they are members of. Okta allows you to map Active Directory or LDAP’s security groups to native Okta groups and, as a result, to automatically provision applications to users based on their membership within AD or LDAP security groups.
When you add a user to your directory, you can place him in a security group, and during automatic synchronization with Okta, that user will be added, and accounts in the applications mapped to that security group will be automatically provisioned on their behalf. Application-specific parameters such as role, profile, and user information are automatically set based on rules defined within the Okta service as well. For example, a rule can be defined within Okta that ensures that all members of the AD/LDAP security group “Sales” are provisioned an account in Salesforce.com and given access to it.
The result is that when a user is added to your directory, all of the tasks required to give him access to his cloud and web-based applications are handled automatically. This greatly reduces the provisioning time for new employees, and allows IT admins to continue to use AD or LDAP as their starting point for user access.
When a user’s Security Group membership changes, the change is detected by the Okta Directory Agent and is relayed to the Okta Service. When this happens, the assignment rules are recomputed. These rules trigger applications to be newly assigned, existing application assignments to be removed, or user properties to be updated on the downstream applications.
New and updated application assignments work exactly the same. All of the steps to provision the account, set up SSO, and update the user’s My Applications home page are handled automatically. Deletions are handled similarly. If a user’s access to an app is removed, he is immediately locked out from using SSO to access that application. The application account is then deactivated by the Okta service, or if that cannot be done automatically, an administrative task is created that must be cleared once the account has been deactivated manually. All of these actions can execute automatically or after confirmation by an Okta administrator.
One-Click Deprovisioning
User deactivation is typically triggered from a standard corporate identity store such as Active Directory or LDAP. With Okta’s centralized deprovisioning, deactivating a user in your user store immediately initiates a deprovisioning workflow to ensure maximum effectiveness in preventing unauthorized access to Okta and other cloud applications. The workflow generates a notification to administrators and guides IT to complete any necessary manual deprovisioning tasks associated with a particular user or application. Further, this workflow also serves as an audit trail; within Okta the entire audit trail is captured for reporting and audit purposes so that you can easily generate historical deprovisioning reports by user or by application.
Single Sign-On for Authenticated Apps
Most enterprises have on-premises web applications that can easily be integrated into Okta’s SSO solution. Many companies also have web applications that use Directory credentials for authentication. These applications are not using Integrated Windows Authentication, but instead require the user to enter their AD or LDAP credentials when they sign in. When Okta is configured to delegate authentication to Active Directory, signing in to these internal web applications can also be automated.
The behind-the-scenes steps that enable SSO for Directory authenticated internal web applications (shown in Figure 10) are:
1. Okta is configured to delegate authentication to AD/LDAP.
2. Customer has on-premises apps authenticating to AD/LDAP.
3. User logs into Okta with AD/LDAP credentials.
4. User accesses App 1 and App 2 with SWA using AD/LDAP credentials.
5. App 1 and App 2 authenticate user against AD/LDAP.
Okta can leverage its Secure Web Authentication protocol to automatically log users into these internal web applications. When an internal web application is configured to delegate authentication to appropriate directory (the same source to which Okta delegates authentication), Okta captures the user’s AD/LDAP password at login and automatically sets that password for that user in any applications that also delegate to AD or LDAP. This allows users to simply click a link to access these applications, and then be logged in automatically.
Note that Okta synchronizes the AD password securely; if the password subsequently changes in AD, this event is captured on login to Okta and immediately updated in the secure password store for that application, ensuring that the next login attempt will be successful.
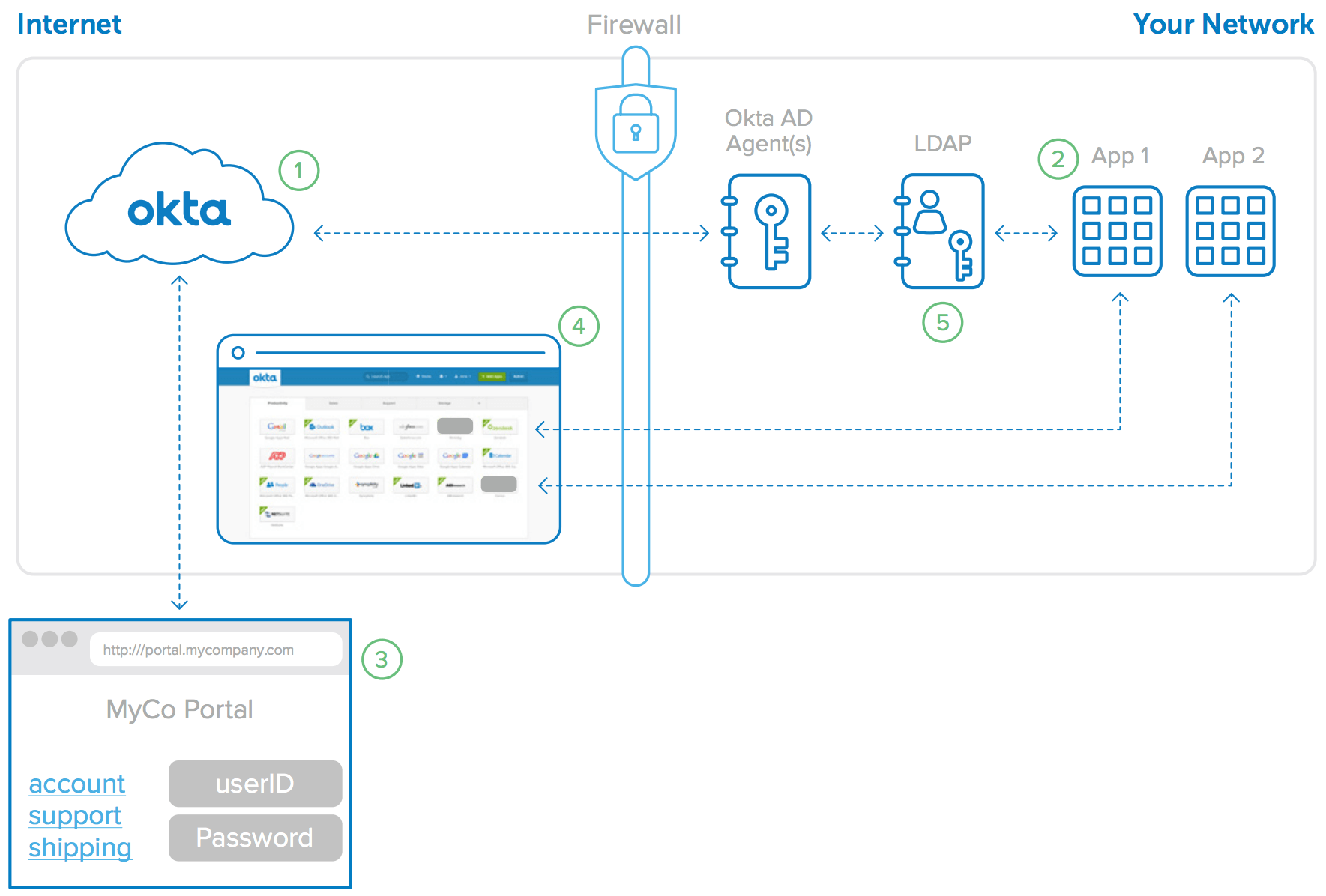
Figure 9: Okta enables SSO for LDAP authenticated internal web applications
Conclusion—Extend Your Directory to the Cloud with Okta
Companies continue to shift their focus from legacy on-premises applications to newer cloud based services. The newer cloud services offer enormous benefits, both in expanded capabilities and in lower overall cost. The question today is not if you can make this transition, but rather how fast can you do it. One of the biggest obstacles in this path is managing user identities in a way that is consistent with users’ and administrators’ experience and expectations. Linking Active Directory or LDAP to cloud services solves this problem, and Okta’s cloud-based identity management solution makes it possible. Okta provides a flexible, highly redundant, and scalable solution for managing cloud identities, and it does so in a service that is easy to set up and is virtually maintenance-free. Let Okta extend your Directory usage to all of your cloud applications—both the apps you use today and the ones you’ll need in the future.
Okta Active Directory Agent Details
The Okta AD Agent is designed to scale easily and transparently. For redundancy a cluster can be created by installing Okta AD Agents on multiple Windows Servers; the Okta service registers each Okta AD Agent and then distributes authentication and user management commands across them automatically. If any agent loses connectivity or fails to respond to commands, it is removed from rotation and the administrator is notified via email. In parallel, the Okta AD Agent will attempt to reconnect to the service using an exponential back-off capped at 1-minute intervals.
System Requirements for Okta AD Agent
The following are minimum system requirements to support the Okta AD Agent:
• Windows Server 2003 R2 or later
• 20 MB of memory for service
• AD Service Account created upon Okta AD Agent installation
Here are suggested system requirements:
• 256 MB of memory for service
• Dedicated AD Service Account with Domain Users permissions
• Separate server from Domain Controller (can be shared)
Okta IWA Web Application Details
Okta IWA is a lightweight IIS web app that enables desktop SSO with the Okta service. The Okta IWA web application installs on Windows Server 2008 in Web Server Role. The installer configures IIS and all Windows components.
System Requirements for Okta IWA Web Application
The following are system requirements necessary to support the Okta IWA web application:
• Windows Server 2008 in Web Server Role
• 50 MB of memory
Okta LDAP Agent Details
The Okta LDAP Agent is designed to scale easily and transparently. For redundancy a cluster can be created by installing Okta LDAP Agents on multiple Windows Servers; the Okta service registers each Okta LDAP Agent and then distributes authentication and user management commands across them automatically. If any agent loses connectivity or fails to respond to commands, it is removed from rotation and the administrator is notified via email. In parallel, the Okta LDAP Agent will attempt to reconnect to the service using an exponential back-off capped at 1-minute intervals.
System Requirements for Okta LDAP Agent
The following are minimum system requirements to support the Okta LDAP Agent:
• Windows Server 2003 R2 or later
• 20 MB of memory for service
• LDAP Service Account created upon Okta LDAP Agent installation
Here are suggested system requirements:
• 256 MB of memory for service
• Dedicated Service Account with Domain Users permissions
• Separate server from Domain Controller (can be shared)
The Okta LDAP agent supports many of the popular LDAP vendors including the following:
• SunOne LDAP 5.2+, 6.*, 7.*
• Oracle Internet Directory
• OpenLDAP
• OpenDJ