The enterprise security landscape is characterized by two contrasting trends, according to Okta’s annual study of billions of anonymized authentications. Organizations are maintaining the steady adoption of traditional defenses while rapidly shifting toward advanced security standards.
The analysis reveals that while overall multi-factor authentication (MFA) adoption within the workforce context (employees accessing apps and tools) has reached 70%, organizations are also making a critical shift: The adoption of phishing-resistant, passwordless authentication has grown by 63%, rising from 8.6% to 14.0% in one year.
The findings also show that these phishing-resistant methods are demonstrably faster and more user-friendly than less secure authenticators, upending the idea that security comes at the expense of user experience.
Key findings include:
Overall, workforce MFA adoption continues its upward trajectory, reaching 70%, but nearly a third of users still lack MFA.
The adoption rate of phishing-resistant authenticators increased 63% in one year, with Okta FastPass adoption nearly doubling.
Phishing-resistant authenticators offer superior security and better user experience than traditional authenticators.
The technology sector leads MFA adoption (87%), while retail saw the biggest growth (up 9 percentage points).
The Asia Pacific region saw the strongest year-over-year growth, with its MFA adoption rate increasing 7 percentage points (from 61% to 68%).
(Note: All data and conclusions in the report are based on analysis of anonymized Okta Workforce Identity data and workforce use cases unless otherwise noted. See the methodology at the end of this article for more information.)
User MFA adoption continues to climb
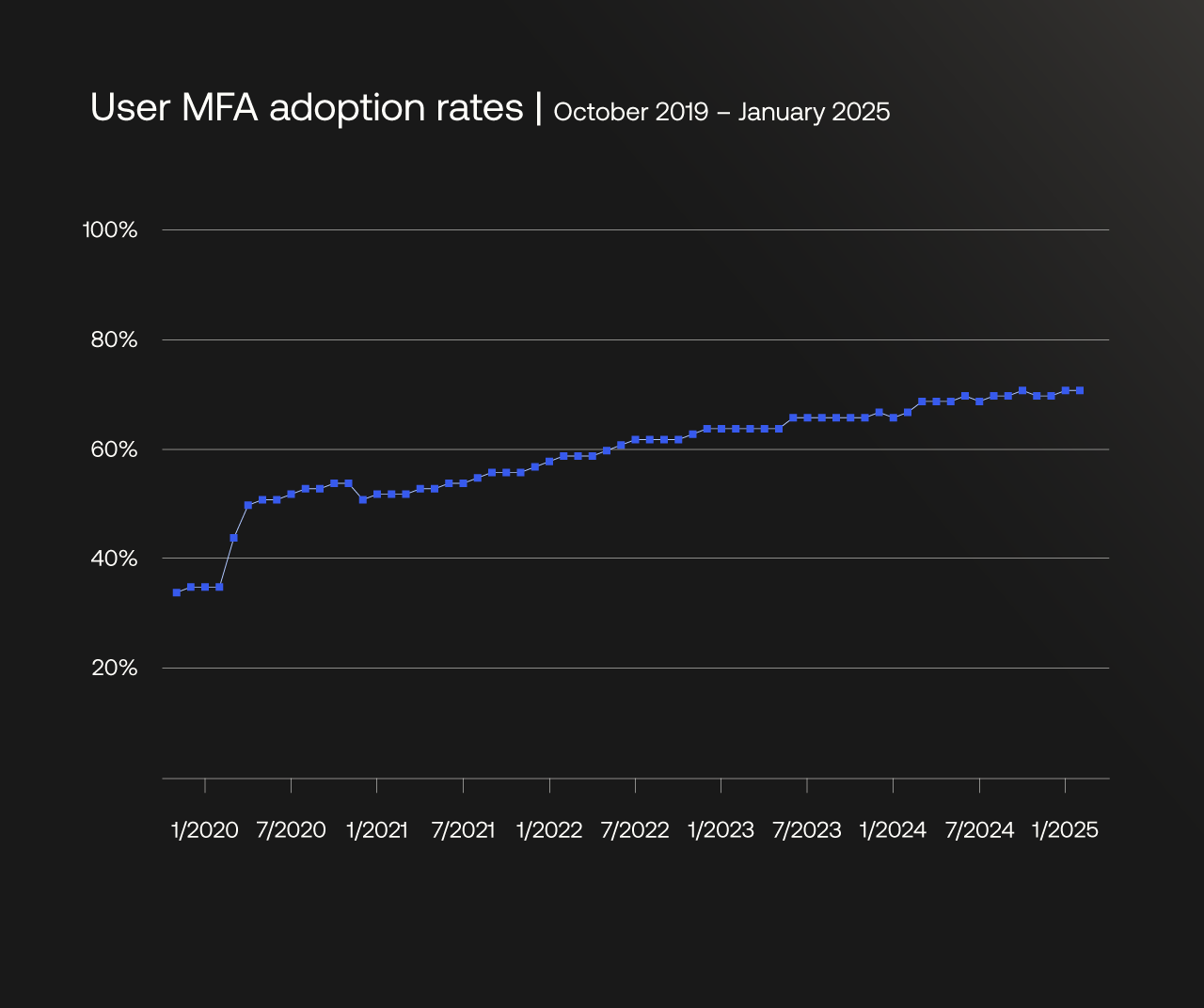 The data reflects monthly user-level MFA adoption rates exclusively for Okta Workforce Identity customers, who use the platform to secure access for their employees, contractors, and partners. Data from Okta Customer Identity, customer-facing use cases, and regulated environments is excluded.
The data reflects monthly user-level MFA adoption rates exclusively for Okta Workforce Identity customers, who use the platform to secure access for their employees, contractors, and partners. Data from Okta Customer Identity, customer-facing use cases, and regulated environments is excluded.
Overall, MFA adoption reached 70% of users as of January 2025, reflecting a mostly steady annual increase since 2020. This upward trend in adoption suggests organizations are increasingly recognizing the need for additional authentication security.
AMER leads in MFA adoption rate, APAC posts the highest growth
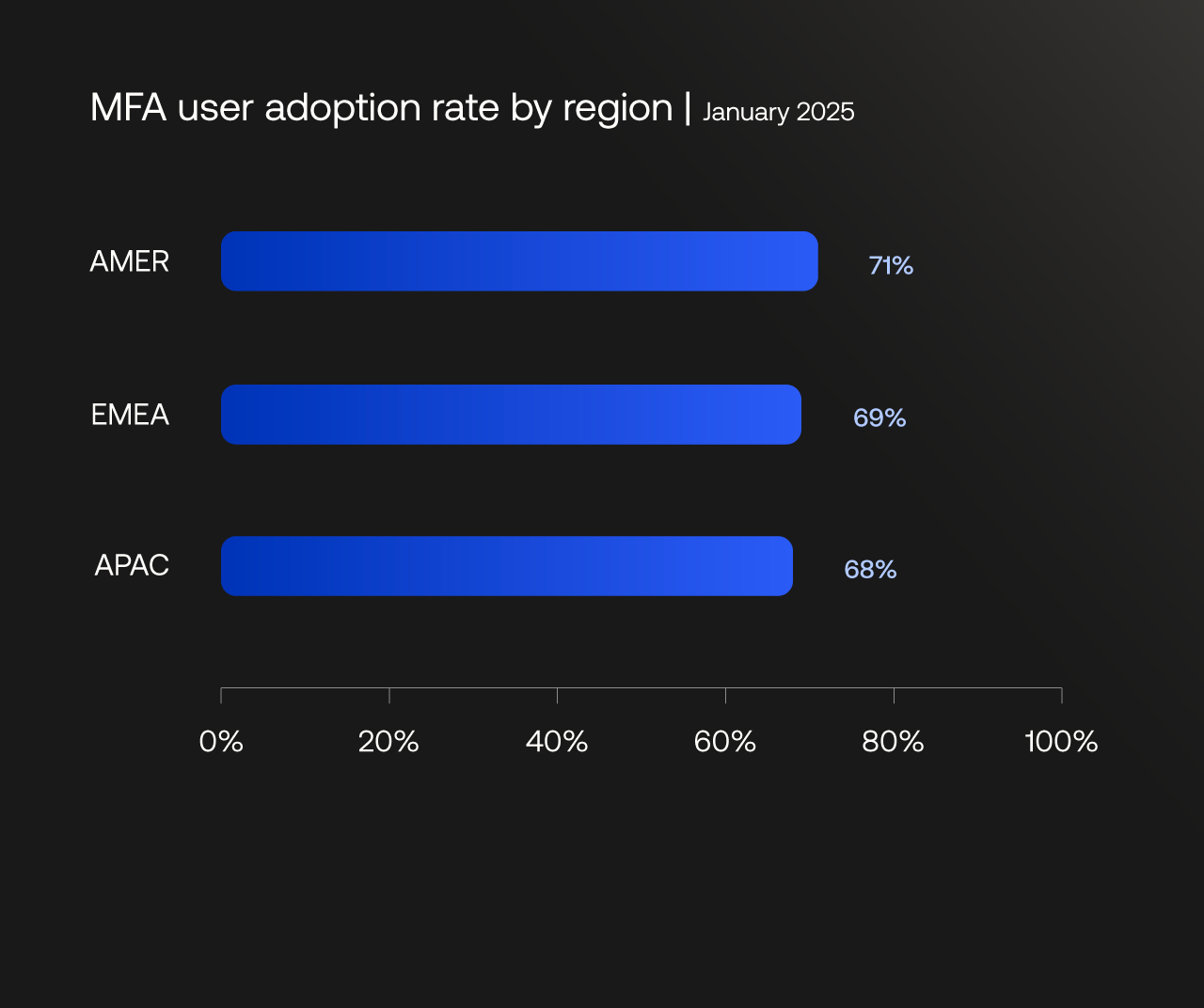 MFA user adoption rates in North, Central, and South America (AMER); Asia-Pacific (APAC); Europe, Middle East, and Africa (EMEA).
MFA user adoption rates in North, Central, and South America (AMER); Asia-Pacific (APAC); Europe, Middle East, and Africa (EMEA).
We observed consistent rates of MFA adoption growth over the last three years across the three regions studied: North, Central, and South America (AMER); Asia-Pacific (APAC); Europe, Middle East, and Africa (EMEA).
APAC saw the strongest year-over-year growth: Its adoption rate increased 7 percentage points (from 61% to 68%), compared to the 2 percentage-point increase in AMER and EMEA. This growth was driven by significant improvements in MFA adoption in Hong Kong (62% to 81%), South Korea (63% to 80%), and Japan (53% to 62%).
This regional growth likely reflects a stronger regulatory focus and rising security awareness across the APAC region, where governments and enterprises are accelerating digital transformation initiatives that emphasize identity protection and modern authentication.
Tech tops MFA user adoption rates, retail posts the highest MFA growth

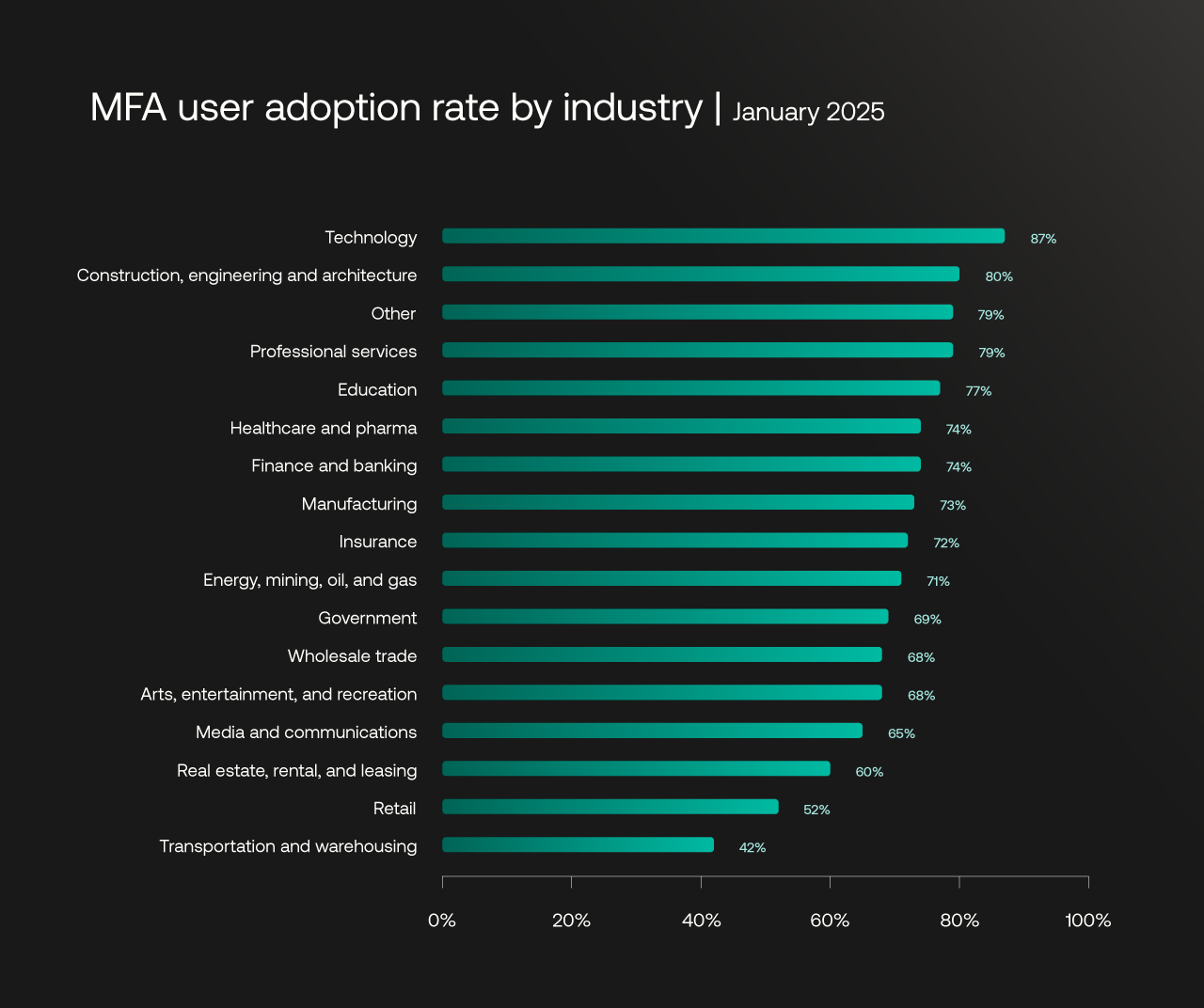 MFA user adoption rates across industries, listed in descending order by rate.
MFA user adoption rates across industries, listed in descending order by rate.
MFA adoption rates are relatively consistent across industries, with the majority falling within the 60% to 80% adoption range. Outliers include transportation and warehousing (42%) and retail (52%) at the low end of adoption and technology at the high end (87%).
The industries with the largest rate of MFA growth year over year included:
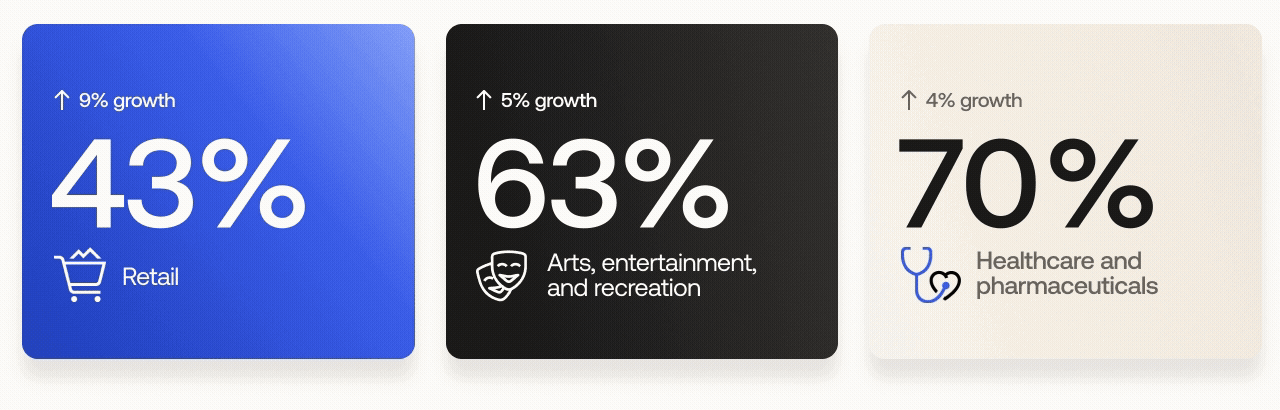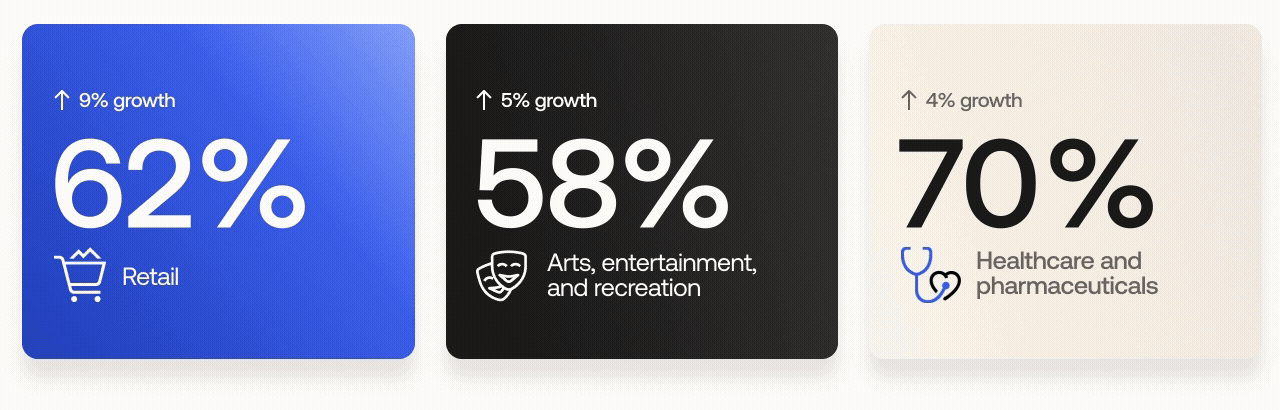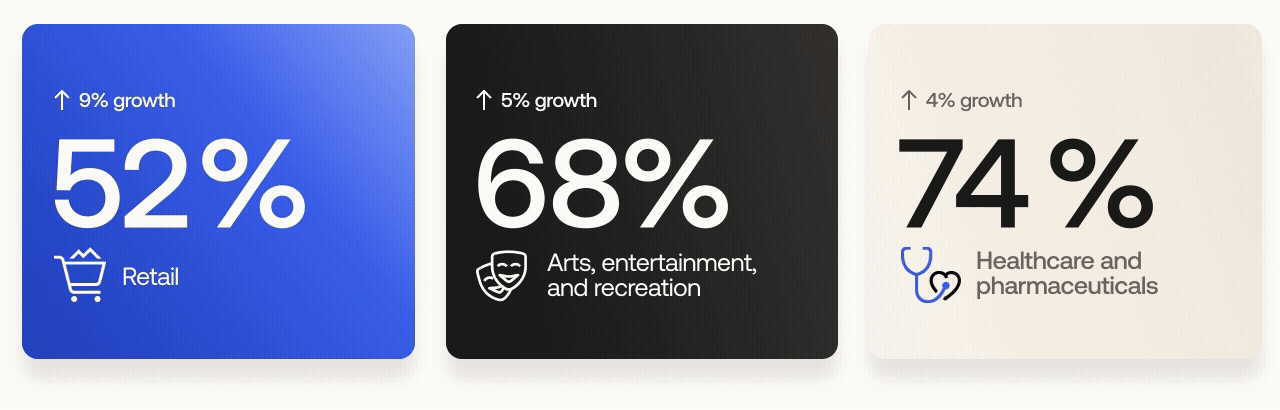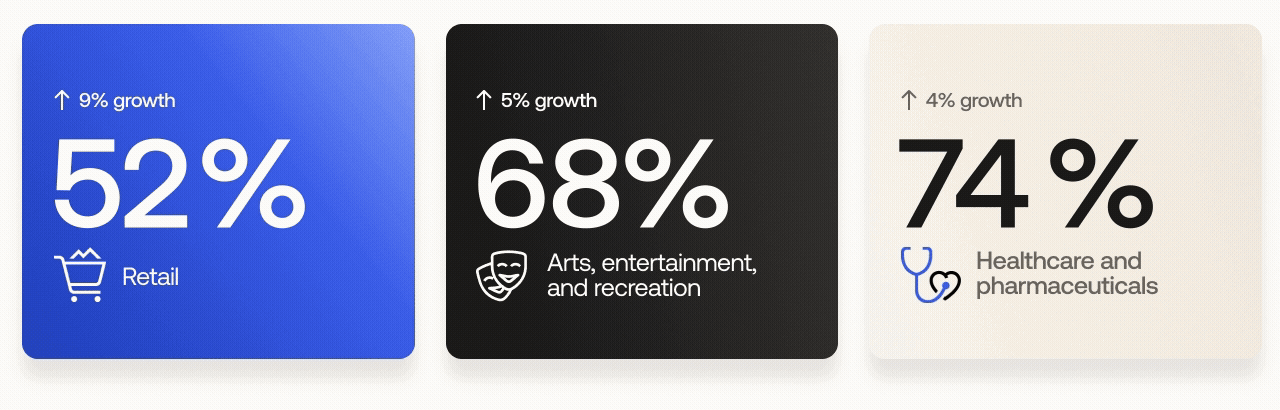
Retail: from 43% to 52%
Arts, entertainment, and recreation: from 63% to 68%
Healthcare and pharmaceuticals: from 70% to 74%
The retail sector experienced the largest growth of all industries, rising 9 percentage points year over year. It was also one of three industries targeted by cybercriminal group Scattered Spider (a.k.a. Scatter Swine, Muddled Libra) in early 2025. We expect further MFA adoption by the retail sector in the wake of these events.
Smaller organizations show higher adoption rates

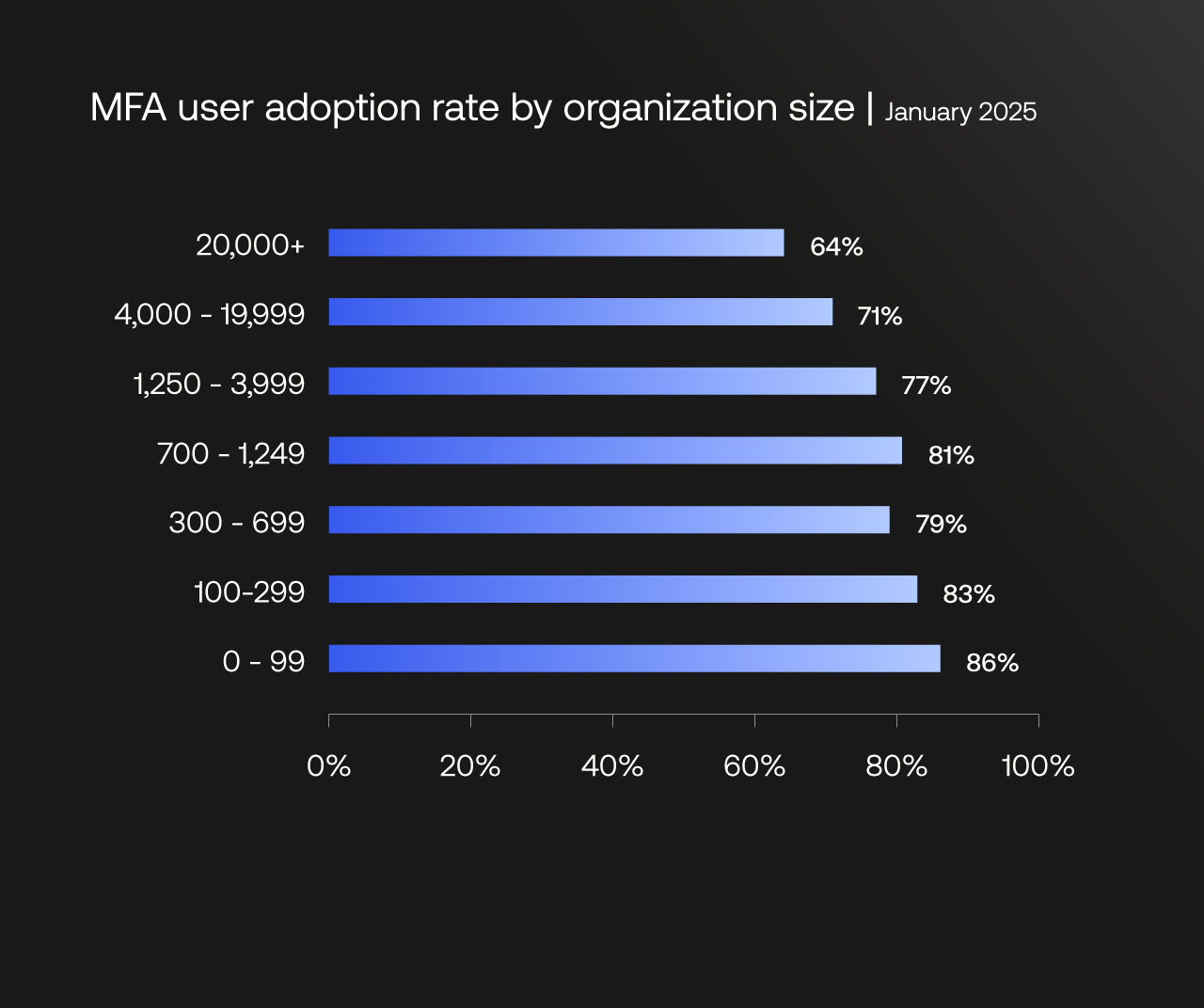 MFA user adoption rates across organizations of different sizes, by number of employees.
MFA user adoption rates across organizations of different sizes, by number of employees.
When we view MFA adoption by organization size, we continue to observe an inverse correlation between the number of employees and the rate of MFA adoption: The larger the organization, the lower the adoption rate.
That said, we observed higher MFA adoption rates since 2024 in organizations with 1,250 to 3,999 employees (from 74% to 77%) and 4,000 to 1,9999 employees (from 67% to 71%). This growth suggests that the tide might be turning, especially as large organizations increasingly adopt centralized identity management platforms.
Passwords reign, but phishing-resistant authenticators gain ground
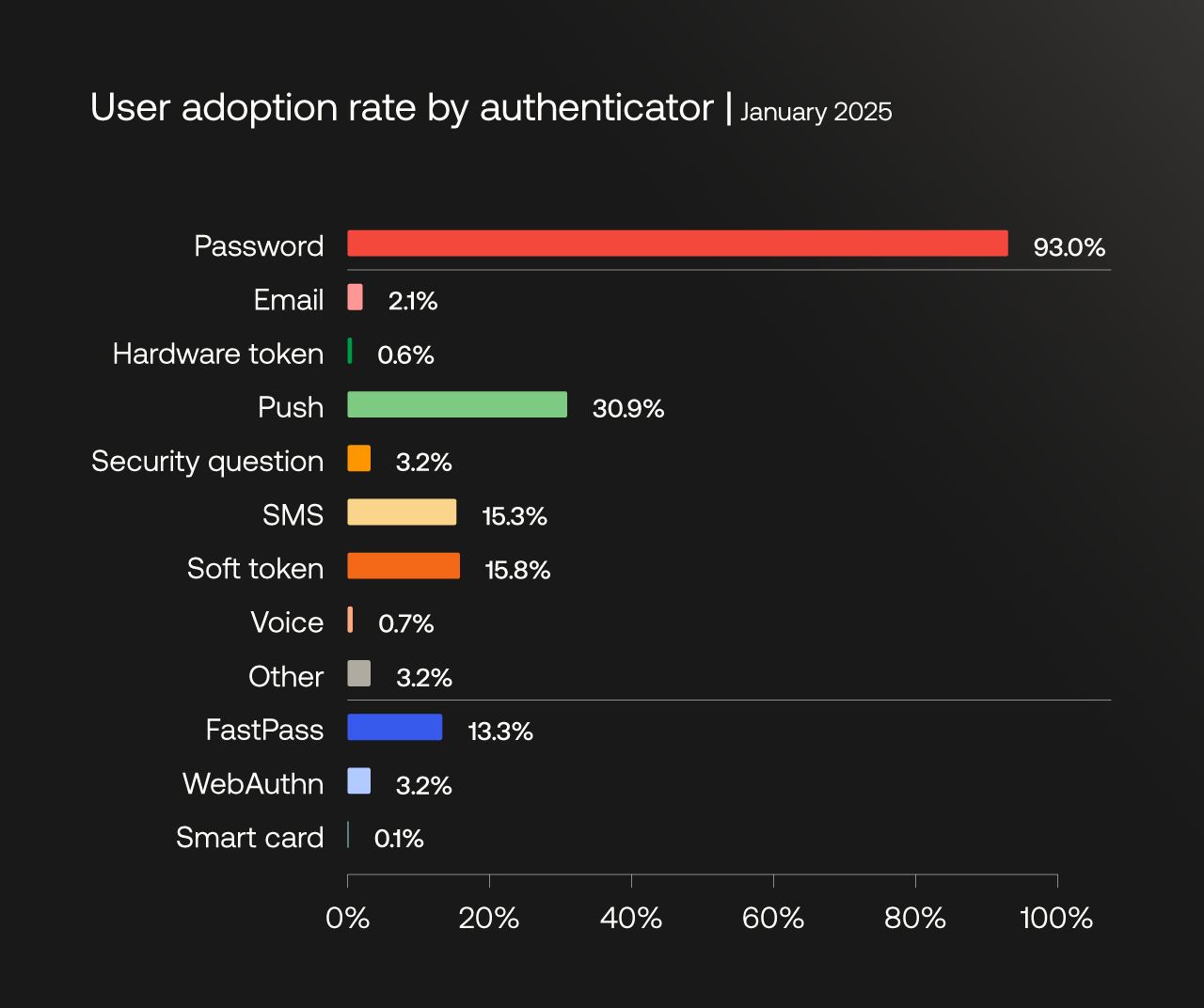 User adoption rates for authenticators available with Okta Workforce Identity. The sum of the adoption rates for each authenticator is higher than the overall MFA adoption rate, given that users may use multiple authenticators.
User adoption rates for authenticators available with Okta Workforce Identity. The sum of the adoption rates for each authenticator is higher than the overall MFA adoption rate, given that users may use multiple authenticators.
While passwords continue to have the highest adoption rate by a wide margin, we see more secure forms of authentication making promising gains.
When we look at phishing-resistant authenticators (FastPass, WebAuthn, and Smart Card) combined, we see a 63% increase in the adoption rate, which rose from 8.6% to 14.0% of users in one year.
This growth indicates that companies are actively replacing vulnerable, traditional security methods, such as SMS and passwords, with higher assurance authenticators. The adoption of phishing-resistant authenticators coincides with a decline in reliance on weaker factors.
Adoption of FastPass — which uses public key cryptography to offer a secure, passwordless sign-in experience — almost doubled, rising from 6.7% to 13.3%.
Usage of low-assurance SMS fell from 17.5% to 15.3%, and overall password usage decreased from 95.1% to 93.0% of users.
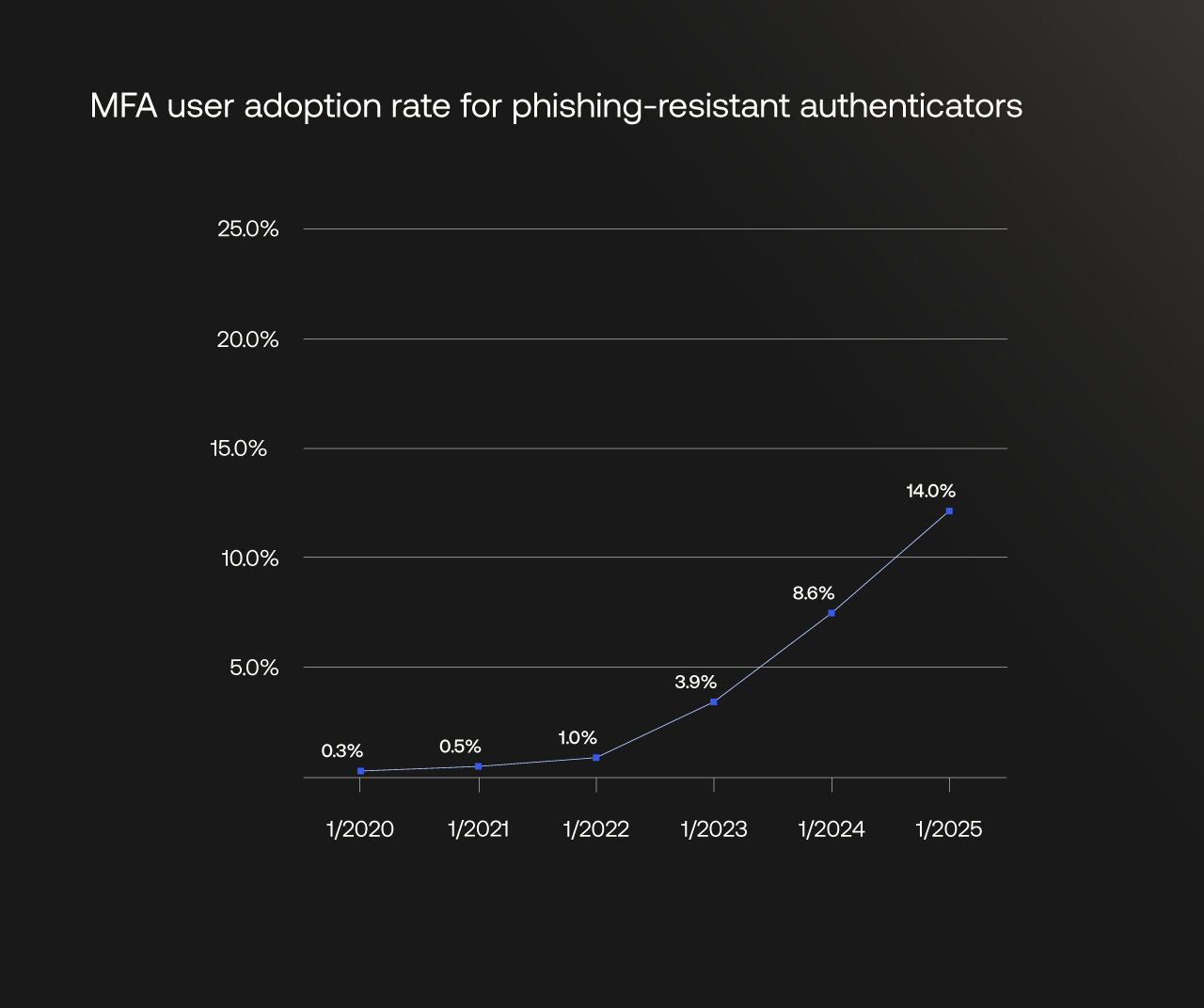 MFA user adoption rates for FastPass, WebAuthn, and Smart Card combined. This overall rate counts a user only once, even if they use multiple phishing-resistant authenticators. It is lower than the sum of individual authenticator adoption rates, where a user utilizing multiple authenticators (such as WebAuthn and FastPass) is counted separately for each.
MFA user adoption rates for FastPass, WebAuthn, and Smart Card combined. This overall rate counts a user only once, even if they use multiple phishing-resistant authenticators. It is lower than the sum of individual authenticator adoption rates, where a user utilizing multiple authenticators (such as WebAuthn and FastPass) is counted separately for each.
Security versus user experience is a false choice
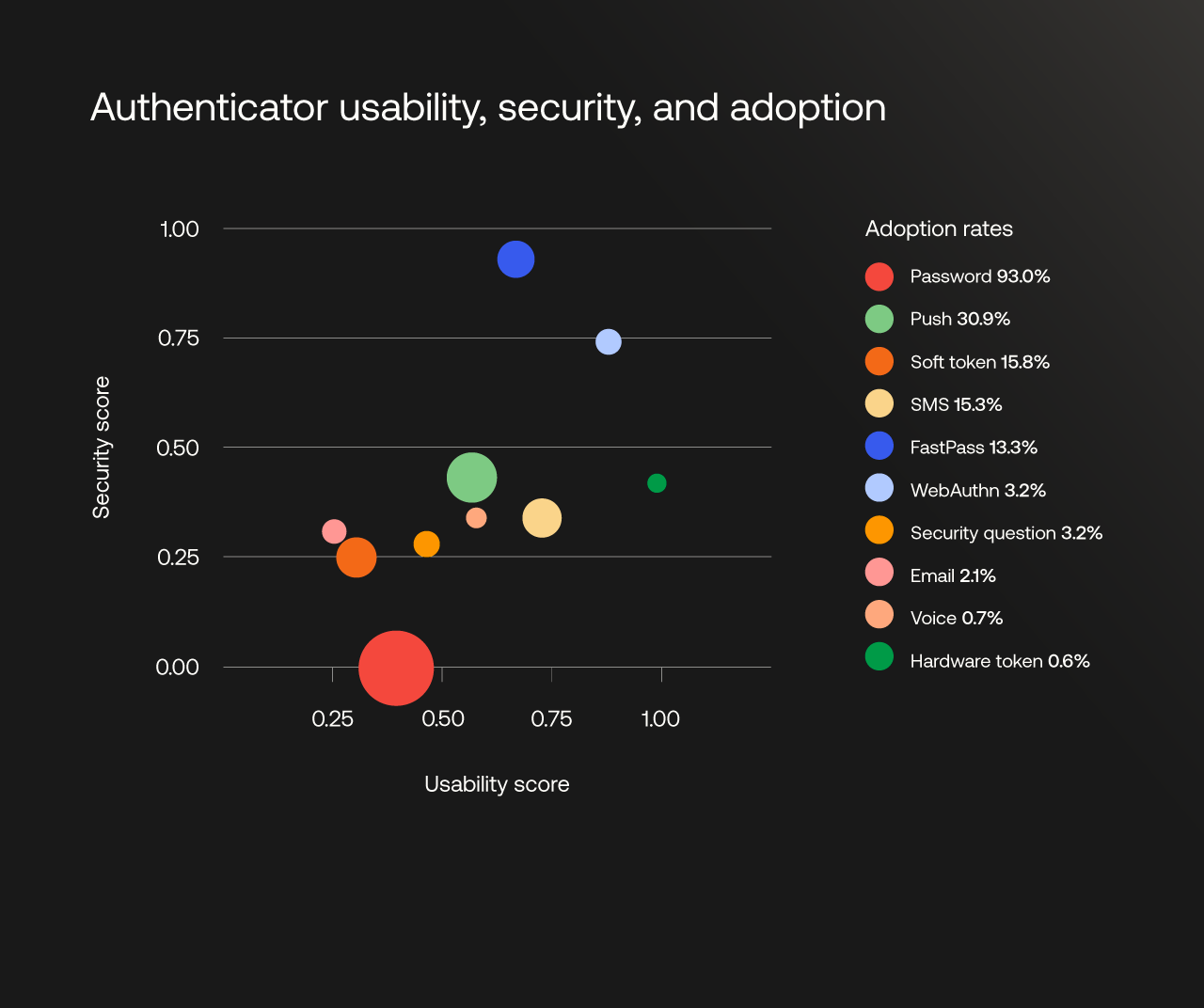 Authenticator usability, security, and adoption for password, email, hardware token, push, security question, SMS, soft token, voice, FastPass, and WebAuthn authenticators as of January 2025. The size of the bubble reflects the authenticator’s adoption rate on a scale of 0% to 100%.
Authenticator usability, security, and adoption for password, email, hardware token, push, security question, SMS, soft token, voice, FastPass, and WebAuthn authenticators as of January 2025. The size of the bubble reflects the authenticator’s adoption rate on a scale of 0% to 100%.
"Security introduces friction" is no longer a foregone conclusion. Analysis of authentication data contradicts this outdated industry assumption by showing that phishing-resistant methods can be more secure and more user-friendly.
To assess the usability and security of each authentication method, we developed scoring rubrics for each. For the usability score, we evaluated backend identity provider metrics, including challenge time, enrollment time, and challenge failure rate. For the security score, we evaluated challenge failure rate, challenge brute-force failure rate, phishing-resistant coverage, and phishing-resistant alert coverage.
We then polled 81 external IT and security practitioners on the relative importance of each metric and weighted the metric based on their responses to arrive at the overall scores. Each authenticator's performance is represented by its usability and security scores shown in the matrix.
We did not assess metrics requiring data external to the identity flow, such as the lead time to purchase the authenticator, qualitative user experience, or data detailing authenticator use during verified malicious credential attacks and account takeovers.
As the matrix demonstrates, phishing-resistant methods WebAuthn and FastPass deliver a superior user experience and have the highest security scores. While lower assurance authenticators, such as password, email, security question, and soft token, score poorly for both security and usability.
Authenticators such as FIDO2 WebAuthn and FastPass perform well by combining multiple factors simultaneously. They provide high assurance by verifying something you have (a possession factor, like a registered device) with something you are (an inherence factor, like a biometric scan). Those who use these methods gain security assurance while enjoying a sign-in process that is demonstrably faster and simpler than traditional, more vulnerable methods.
Users are starting to take note, with some ditching the password altogether. Our study found that in January 2025, 7% of users did not use a password for any sign-ins, validating that enterprise-scale password elimination is achievable today. While the number may seem small, it demonstrates exciting potential: Passwordless for enterprises is possible now.
Policy, proof, and the new security baseline
Our findings confirm that the industry has passed the point of treating MFA as an optional enhancement. It is critical for businesses to stay secure. Given the success rate of social engineering and phishing campaigns, the accelerated adoption of phishing-resistant authentication methods is a necessary market response.
The old argument that robust security must come at the expense of user productivity is not supported by the data. The security landscape is no longer about compromise, but transformation. Major technology companies, including Salesforce, GitHub, AWS, and Microsoft, are signaling this shift by committing to mandatory MFA enforcement for their privileged users, indicating that MFA is transitioning from a recommended best practice to a mandatory security baseline.
Policy can be a powerful driver of change. For example, Okta's mandatory MFA policy for administrator console access in 2024 resulted in 100% adoption among customer admins by August 2025.
Phishing-resistant authentication is secure, user-friendly, and demonstrably achievable. It is critical for protecting organizations against today's threats while reducing user friction.
5 tips to improve your authentication strategy
To successfully navigate this security transformation, leaders must transition from discussing best practices to mandating new standards. Organizations should focus on these requirements:
Prioritize phishing resistance: Mandate phishing-resistant MFA for all sensitive access, while eliminating low-assurance methods (like SMS) from all sign-on policies.
Elevate MFA as a risk metric: Treat the adoption of MFA, particularly phishing-resistant MFA, as a C-suite and board-level risk metric, enabling visibility and accountability for organizational security posture.
Adopt a Zero Trust framework: Shift access control to a per-session, least-privilege basis, dynamically evaluating the user, the device's posture, and the network context at the moment of access and throughout the session.
Secure the full user lifecycle: Apply phishing-resistant authentication methods to user enrollment and account recovery flows to prevent attackers from using these entry points for account takeover.
Plan for password minimization: Develop a clear, long-term strategic plan to phase out the reliance on passwords as a primary factor across the enterprise.
Methodology: About the data
The study is based on data from Okta Workforce Identity as of January 2025, with the exception of the MFA user adoption rate over time, which extends from October 2019 to January 2025.
The data was anonymized and aggregated from billions of monthly authentications and verifications originating from countries worldwide. The report methodology has been updated this year to reflect only commercial customer environments, excluding data from regulated environments. The charts and stats in this report, including data from prior years, reflect the new methodology.
Customers and their employees, contractors, partners, and clients use the Okta Platform to securely log in to devices, websites, applications, and services, leveraging security features to protect their data. These organizations span every major industry and vary in size, from small businesses to some of the world’s largest enterprises.
Company size is defined by the number of full-time employees in the company. Company industry taxonomy aligns with the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Company size, industry, and geographic region were all validated using third-party resources.
All user adoption rate metrics are determined by the percentage of users who signed in using the studied authenticators over a one-month period.
Unless otherwise noted, this analysis focuses exclusively on Okta Workforce Identity data and workforce use cases. It does not include Okta Customer Identity data.







