Three Ways to Modernize Identity
Why choose Okta and AWS
Enterprises are currently undergoing high-level initiatives around digital transformation, migrating assets and processes to the cloud in order to support corporate agility and modernize IT and security. The process can reduce the costs of infrastructure management and maintenance, remove legacy identity as a constraint, reduce IT spend on expensive client access licenses, and simplify and secure user access—especially remote user access—to IT services across cloud and on-premises assets.
As companies look to isolate and unwind their legacy directory services, Okta and AWS combine efforts to support safely moving any workload type to the cloud, whether that be via replacing, rehosting, replatforming, or refactoring.
The Okta Identity Cloud is a leading cloud-based identity platform that cloudifies a company’s identity infrastructure as part of a broader modernization of IT. Moving identity to the cloud allows for secure, appropriate user access to SaaS, public cloud, and premises-based applications from anywhere in the world via trusted endpoints.
AWS Directory Service for Microsoft Active Directory, also known as AWS Managed Microsoft AD, enables companies to run directory-aware workloads in the AWS Cloud, including Microsoft SharePoint and custom .NET and SQL server-based applications. It also provides seamless access to AWS services such as Amazon RDS for SQL Server and Amazon FSx for Windows File Server. AWS Managed AD can be run standalone— as a company’s only AD environment—or can be an extension of a company’s legacy on-premises identity infrastructure.
In this guide, we’ll examine how Okta and AWS work together to support and accelerate enterprise cloud migration in three specific deployment scenarios: 1) adding Okta to an AWS Managed Microsoft AD deployment that’s the primary domain, 2) adding Okta when extending an existing AD into AWS, and 3) adding AWS Managed Microsoft AD to an existing Okta deployment.
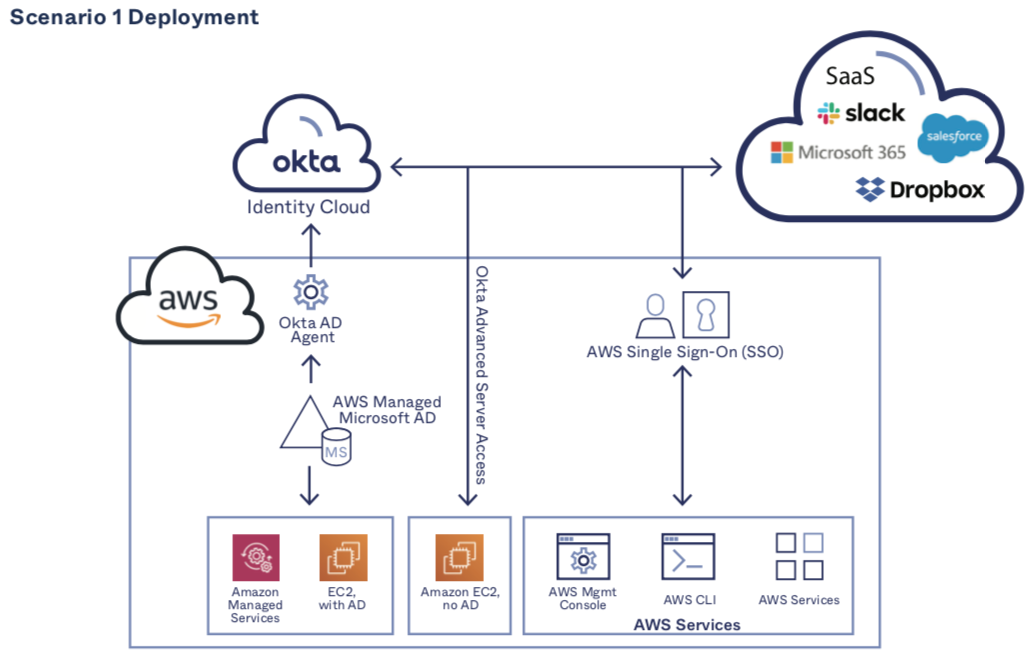
Scenario #1: Adding Okta Identity Cloud to an Existing AWS Managed Microsoft AD Deployment that’s the Primary Domain
In this scenario, organizations are using AWS Managed Microsoft AD as their primary AD environment, connecting any limited premise-based infrastructure to AWS Managed Microsoft AD. Here’s how adding Okta to this deployment can help further its goals.
Goal: Adding federated authentication and user lifecycle management to SaaS applications like Office 365
As with on-premises based AD, supporting user authentication on an application-by-application basis using AD credentials is complex—and often not possible. All leading SaaS providers, including Microsoft 365, support SAML or OIDC-based federated authentication, an approach that results in one connection from Okta to an AWS Managed Microsoft AD environment that’s shared by all SaaS applications via Okta. Users use their AWS Managed Microsoft AD credentials to login to Okta, and then Okta delegates authentication to AWS Managed Microsoft AD.
To connect Okta to AWS Managed Microsoft AD, the Okta Active Directory agent is installed on an EC2 instance within a company’s AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), and that agent connects outbound to the company’s Okta tenant. This integration enables the use of AD credentials to access all SaaS apps, with no additional inbound connections to the VPC.
In addition to federated authentication, Okta automates user adds/updates/deletes in downstream systems. This can be done either through a combination of SCIM-based user synchronization or through Okta Workflows which provides a no-code visual designer for more complex user flows. For extensibility, an Okta Workflow can execute Lambda functions to handle even the most complex flows.
Goal: Expanding access to AWS SSO and other AWS services
For companies with user groups outside of AWS Managed Microsoft AD, the Okta Universal Directory can provide a single aggregated directory (Managed AD, or on- premises AD, LDAP, or HR systems) from which to control access to AWS SSO and other AWS services. This is done by connecting Okta and AWS SSO via SAML.
Goal: Deploying unified Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for improved security
Connecting applications to the Okta Identity Cloud has an additional benefit: Those applications inherit Okta’s MFA. With Okta MFA, companies can mix and match legacy and modern MFA within their environment and centrally manage MFA policies for all resources, including VPN, SaaS, cloud and premises.
Goal: Removing specific user communities from Active Directory
Most organizations today include contractors, seasonal workers, or other 3rd parties among their aggregate workforce. In many instances those personnel require only a limited set of applications, or may be accessing those applications from mobile devices or devices not owned by the company. With Okta, these user communities’ credentials can live in Okta alongside those mirrored from AD into Okta. This reduces the security surface area by reducing AD accounts, while eliminating the need for AD client access licenses for these user sets.
Goal: Providing an alternative model for administrative access to servers
Okta Advanced Server Access (ASA) provides secure administrative access to Linux and Windows servers without the need to join those servers to a domain and limiting Client Access License requirements. As users join, move, and leave, and servers’ fleets are expanded or contracted, Okta ASA automates the add/change/delete function of local administrative accounts on Windows and Linux servers and mints tightly scoped certificates for each user session.
Goal: Managing customer and partner identities
As companies expose digital experiences to customers and partners, they need a highly secure authentication experience in place, complete with self-service password resets, multi-factor authentication, etc. Many companies initially leveraged Microsoft Active Directory for their user communities, but are looking to make a change for performance, scalability, flexibility, and many other reasons. Okta’s Universal Directory is built to handle these user communities and their unique requirements. Okta’s functionality can be plugged into a customer’s existing environment in a number of ways, allowing for customer-branded, simple and secure experiences.
Okta and AWS Managed AD for Modernizing Identity
Scenario #2: Adding Okta Identity Cloud when Extending an Existing AD Infrastructure into AWS via AWS Managed Microsoft AD
In this scenario, organizations with legacy, premise-based AD instances are extending their AD environment into AWS in support of workload migration to the cloud or to support the use of AWS services like Amazon RDS for SQL Server and Amazon WorkSpaces. Customers extending their existing AD infrastructure to AWS via AWS Managed AD are typically doing so to solve challenges like these:
- Permit the workforce to sign into AWS services with AD credentials seamlessly
- Havedomainservicesco-locatedwithdependentworkloadstoimproveperformance
- Manage EC2 instances
- Establish security isolation between on-premises and cloud
- Accelerate AD-aware workloads migration and deployments in AWS
- Simplify AD management across geographies
- Eliminate the overhead of AD management in the cloud
Adding Okta to this kind of deployment can help further all the goals named in Scenario 1 above, as well as the following:
Goal: Limiting AD sprawl for companies looking to leverage AD only where required
Certain workloads require AD, and AWS Managed Microsoft AD handles these use cases. In cases where AD is not required, though, many companies would prefer to take a modern approach to identity and not deepen their legacy dependency any further. This is especially true for new workloads being developed, where a modern, federated approach is often preferred. In cases like these, Okta manages these workforce identities without adding to AD resource utilization or extending legacy dependency.
Goal: Centralizing access to cloud- and premises-based applications
Companies migrating to the cloud will typically operate in a hybrid model for a number of years, as many workloads may not be worth migrating. (For example, if the plan is to EOL them in a medium time horizon, or if they are only utilized by a very small user community.) For cases like these, the Okta Access Gateway is Okta’s bridge from the cloud into the data center, seamlessly connecting users to workloads running on premises. The Access Gateway supports header-based authentication and protocol translation to provide familiar and secure access to many applications, like the Oracle e-Business Suite. Once on-premise applications are connected to Okta, those workloads can be migrated to the cloud with no change in the end user access experience.
Okta and AWS Managed AD for Modernizing Identity
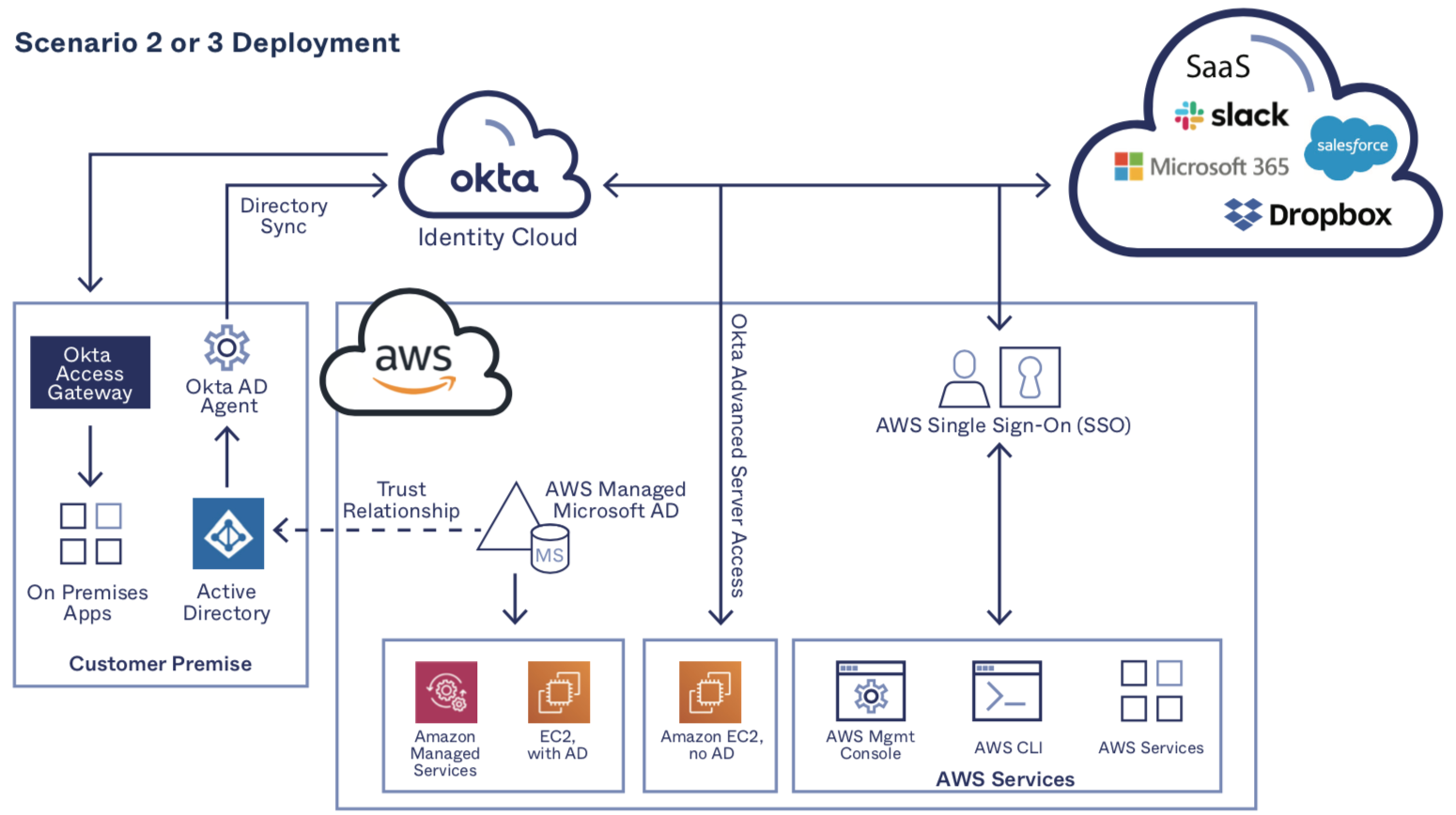
Scenario #3: Adding AWS Managed Microsoft AD to an Existing Okta Identity Cloud Deployment
In this scenario, a customer is already using the Okta Identity Cloud, and has made the investment in cloudifying their identity infrastructure. The majority of customers are using Okta to abstract identities away from Active Directory, connect all SaaS to Okta, and automate user lifecycle management with Okta. And many of them are also using the Okta Access Gateway to expand access through Okta to premise-based applications as well.
For customers in this situation, adding AWS Managed Microsoft AD to an Okta deployment can help with goals like the following:
Goal: Managing Windows EC2 instances
The Okta Identity Cloud provides user access to Windows instances, as described above. Okta does not provide an alternative to AD Group Policy Objects for OS policy management, but AWS Managed Microsoft AD provides the infrastructure to satisfy this requirement.
Goal: Providing seamless access to Windows-based AWS services
In support of key customer requirements, AWS has managed versions of key directory- aware services, including:
- Amazon Connect
- Amazon EC2
- Amazon FSx for Windows File Server
- Amazon RDS for MySQL
- Amazon RDS for Oracle
- Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL
- Amazon RDS for SQL Server
- Amazon WorkSpaces
- AWS Client VPN
- AWS Single Sign-On
These services are designed to leverage Active Directory and can be integrated seamlessly with AWS Managed Microsoft AD.
Goal: Supporting migration of AD-dependent workloads to the cloud
Beyond the operating system itself, many workloads—particularly Microsoft workloads like Microsoft SQL Server—are most easily managed by administrators through domain accounts. By leveraging a trust relationship from the Managed AD domain back to a company’s primary domain, this familiar access can be provided.
Goal: Providing end-users with AD-credential-based access to AD-reliant applications
Beyond administrator access, there is a limited set of applications that require direct integration with AD for user authentication, e.g. Amazon WorkSpaces. By having both Okta and AWS Managed AD, users maintain a single set of credentials and access is simple, seamless, and secure.
About Okta
Okta is the leading independent identity provider. The Okta Identity Cloud enables organizations to securely connect the right people to the right technologies at the right time. With more than 7,000 pre-built integrations to applications and infrastructure providers, Okta provides simple and secure access to people and organizations everywhere, giving them the confidence to reach their full potential. More than 10,000 organizations, including JetBlue, Nordstrom, Siemens, Slack, T-Mobile, Takeda, Teach for America, and Twilio, trust Okta to help protect the identities of their workforces and customers. To learn more, visit okta.com.